Schizophrenia: A Complex and Misunderstood Disorder

Table of Contents
Understanding the Nature of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and emotional responsiveness. It affects an estimated 20 million people worldwide, causing significant distress and impairment in their daily lives. While its exact cause remains unknown, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurobiological factors contribute to the development of this condition.
One of the defining features of schizophrenia is the presence of psychosis, which involves a detachment from reality. Individuals with this disorder may experience hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and reduced emotional expression. These symptoms can severely impact their ability to function in society, leading to social isolation, unemployment, and a decreased quality of life. It is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of schizophrenia early on to facilitate prompt diagnosis and intervention, as early treatment can significantly improve outcomes. However, due to the complexity and heterogeneity of the disorder, diagnosing schizophrenia can be challenging, requiring a comprehensive assessment and evaluation by mental health professionals. Understanding the nature of schizophrenia is essential for both individuals affected by the condition and their families to navigate the diagnostic process effectively and access appropriate treatment and support.
Historical Perspectives on Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia is a complex psychiatric disorder that has been recognized and studied for centuries. The historical perspectives on schizophrenia provide invaluable insights into the changing understanding and perceptions of this condition throughout time.
Early historical accounts of schizophrenia can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans. These civilizations attributed the symptoms of schizophrenia to spiritual possession or divine intervention. However, it was not until the 19th century that Emil Kraepelin, a German psychiatrist, made significant advancements in categorizing and defining schizophrenia as a distinct illness. His work laid the foundation for modern understanding and diagnosis of the disorder.
Over the years, the understanding of schizophrenia has evolved as researchers and scientists continue to uncover the underlying causes and mechanisms behind the condition. From Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective to the emergence of the biological model, multiple theories and treatment approaches have shaped the historical journey of schizophrenia. Today, a comprehensive understanding of schizophrenia incorporates a biopsychosocial model, recognizing the interplay between genetic factors, neurochemical imbalances, and environmental influences. This historical context is crucial in informing current research and treatment strategies for individuals living with schizophrenia.
The Prevalence and Impact of Schizophrenia in Society

Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that significantly impacts individuals and society as a whole. Its prevalence in society is higher than one might think, with estimates suggesting that about 1% of the global population is affected by this condition. This means that there are millions of individuals struggling with schizophrenia, and their needs must be addressed for the betterment of our society.
The impact of schizophrenia goes beyond the individual diagnosed with the disorder. It also affects their families, friends, and communities. The burden of caring for a loved one with schizophrenia can be overwhelming, both emotionally and financially. Moreover, the inability to work or maintain stable relationships often leads to social isolation and a diminished quality of life for individuals with schizophrenia. The societal cost of schizophrenia is significant, with studies estimating that it accounts for a substantial portion of healthcare expenses and lost productivity.
Understanding the prevalence and impact of schizophrenia in society is crucial for the development and implementation of effective support systems and interventions. By recognizing the magnitude of the problem and the challenges faced by individuals with schizophrenia, we can work towards reducing stigma, improving access to care, and providing the necessary support to enhance their overall well-being. Further exploration of this topic will shed light on the specific strategies and initiatives needed to address the unique needs of individuals living with schizophrenia and create a more inclusive and supportive society for all.
Genetic Factors and Schizophrenia: Unraveling the Complexities
Schizophrenia is a complex psychiatric disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. While the precise cause of schizophrenia remains unknown, researchers have made significant strides in understanding the genetic factors that contribute to its development. Unraveling the complexities of the genetic basis of schizophrenia is crucial in order to better comprehend the underlying mechanisms and ultimately pave the way for improved diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
Numerous studies have suggested that genetic factors play a substantial role in the etiology of schizophrenia. Twin and family studies have consistently demonstrated a higher concordance rate in monozygotic twins compared to dizygotic twins, providing strong evidence for a genetic predisposition. These findings have led researchers to focus on unraveling the specific genes that may be involved in the development of schizophrenia. Recent advancements in genetic research techniques, such as genome-wide association studies (GWAS), have enabled scientists to identify several genetic variations associated with schizophrenia. However, it is important to note that these genetic variations only confer a modest increase in the risk of developing schizophrenia, indicating that multiple genes and environmental factors likely interact to contribute to the disorder.
Understanding the genetic complexities of schizophrenia is a challenging task due to the polygenic nature of the disorder. It is believed that a combination of common genetic variants with small effect sizes and rare genetic mutations with larger effect sizes contribute to the overall risk of schizophrenia. The identification of individual genes associated with schizophrenia has been a complex and ongoing process, with researchers discovering several susceptibility genes that are involved in various biological pathways, such as neurodevelopment, synaptic function, and immune response. However, the precise roles of these genes and their interactions with other genetic and environmental factors are still being elucidated.
In conclusion, the unraveling of the genetic complexities underlying schizophrenia is a crucial step towards advancing our understanding of the disorder. Although significant progress has been made in identifying genetic variations associated with schizophrenia, further research is needed to uncover the specific mechanisms through which these variations contribute to the development and progression of the disorder. Enhancing our knowledge of the genetic factors involved in schizophrenia holds the potential to revolutionize diagnostic approaches, facilitate personalized treatment strategies, and ultimately improve the lives of individuals affected by this debilitating condition.
Certainly! Here’s the relation between “Genetic Factors and Schizophrenia” presented in a table format:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heritability Estimates | Studies indicate a significant genetic contribution to schizophrenia, with higher risk observed among individuals with affected family members. |
| Candidate Genes and GWAS | Research has identified candidate genes associated with schizophrenia through genome-wide association studies, shedding light on its genetic basis. |
| Neurobiological Mechanisms | Genetic factors influence various neurobiological processes implicated in schizophrenia, including neurotransmitter systems and brain development. |
| Genetic Markers and Risk Prediction | Advances in genetics have led to the identification of genetic markers and risk variants, aiding in the prediction and understanding of schizophrenia. |
Neurotransmitters and Brain Abnormalities in Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex and multifaceted mental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Extensive research has been conducted to understand the underlying neurobiological abnormalities that contribute to the development and progression of this condition. One area of focus is the role of neurotransmitters and brain abnormalities in schizophrenia.
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the brain that facilitate communication between nerve cells. In individuals with schizophrenia, there is evidence of imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine and glutamate. Dopamine is associated with the brain’s reward and pleasure centers, and abnormalities in its regulation have been implicated in the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions. On the other hand, glutamate, which is involved in learning and memory processes, may be disrupted in individuals with schizophrenia, contributing to cognitive impairments.
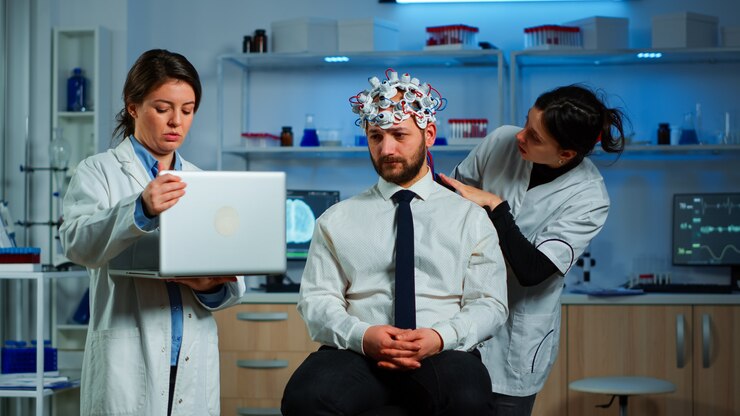
In addition to neurotransmitter imbalances, brain abnormalities have also been observed in individuals with schizophrenia. Brain imaging studies have shown structural differences, including reduced gray matter volume and abnormalities in certain brain regions, such as the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. These structural abnormalities may underlie the cognitive, emotional, and perceptual disturbances experienced by individuals with schizophrenia.
While the exact mechanisms linking neurotransmitter imbalances and brain abnormalities to the development of schizophrenia are still being explored, these findings provide valuable insights into the biological basis of this complex disorder. Understanding the role of neurotransmitters and brain abnormalities in schizophrenia is crucial for the development of more targeted and effective treatment strategies to alleviate the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that affects approximately 1% of the population worldwide. It is important to be aware of the early warning signs and symptoms of schizophrenia in order to seek timely intervention and support. While the specific symptoms can vary from person to person, there are some common signs that may indicate the onset of this condition.
One of the primary early warning signs of schizophrenia is experiencing hallucinations or delusions. These can be auditory, visual, or even tactile in nature. Individuals may hear voices that are not present or believe in ideas that are not based in reality. These hallucinations and delusions can cause significant distress and interfere with daily functioning. It is crucial to seek medical attention if you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms.
In addition to hallucinations and delusions, changes in thinking and perception can also be early indicators of schizophrenia. Individuals may struggle with organizing their thoughts, finding it difficult to concentrate or maintain a coherent conversation. They may also experience disordered thinking, where their thoughts seem jumbled or illogical. Furthermore, individuals with schizophrenia may exhibit changes in their emotions and behavior, such as a decreased ability to experience pleasure or a noticeable shift in their social interactions.
It is important to note that identifying these early warning signs and symptoms does not necessarily mean that someone has schizophrenia. Other medical conditions and factors can contribute to similar symptoms, underscoring the importance of a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals living with schizophrenia, and it is essential to approach these signs with empathy, understanding, and a commitment to supporting those in need.
Diagnosis and Assessment: Navigating the Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process for schizophrenia can be complex and challenging, requiring careful assessment and evaluation. It often involves a comprehensive examination of an individual’s symptoms, medical history, and family history, as well as an assessment of their thoughts, behaviors, and emotions. A thorough understanding of the diagnostic criteria established by reputable medical organizations, such as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), is essential for accurate diagnosis.
During the diagnostic process, healthcare professionals may use various tools and assessments to gather information and evaluate the presence of symptoms associated with schizophrenia. These may include structured interviews, questionnaires, rating scales, and clinical observations. The purpose of these assessments is to gather objective data and establish a clear picture of an individual’s symptoms, their frequency, and their impact on their daily functioning. Additionally, in some cases, medical tests such as blood tests or brain imaging may be conducted to rule out other potential causes of symptoms or to gather additional information.
It is important to note that diagnosing schizophrenia is not a one-size-fits-all approach. The symptoms and experiences of individuals can vary significantly, and the diagnostic process requires careful consideration of each person’s unique circumstances. Additionally, mental health professionals must be mindful of potential biases and limitations in the diagnostic process, ensuring that a comprehensive and holistic approach is taken to accurately assess and diagnose this complex condition. By navigating the diagnostic process with empathy, expertise, and thoroughness, healthcare professionals can provide individuals with the necessary support and set a foundation for a targeted and effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Schizophrenia: Medications and Therapies
Schizophrenia is a complex and challenging mental health condition that requires comprehensive treatment. Fortunately, there are a range of effective treatment options available, including medications and therapies, that can help individuals living with schizophrenia manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Medications, such as antipsychotics, are often the first line of treatment for schizophrenia. These medications work by targeting the imbalances in brain chemicals, particularly dopamine, which are associated with the symptoms of schizophrenia. Antipsychotics can help reduce hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thoughts, allowing individuals to regain control over their lives.
In addition to medications, therapies play a vital role in the treatment of schizophrenia. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is frequently used to help individuals develop coping strategies and challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs. This type of therapy can be incredibly beneficial in reducing symptoms, improving functioning, and enhancing overall well-being.
Furthermore, family therapy is often recommended for individuals with schizophrenia, as it can help educate family members about the condition and provide them with the skills and support necessary to effectively assist their loved ones. Additionally, social skills training and vocational rehabilitation can help individuals with schizophrenia develop essential life skills, improve their social interactions, and gain greater independence.
It is important to note that treatment for schizophrenia is highly individualized, and what works for one person may not work for another. Medication dosages and types, as well as therapy approaches, may need to be adjusted over time to ensure optimal symptom management.
In conclusion, a combination of medications and therapies is often the best approach for treating schizophrenia. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with schizophrenia can find a treatment plan that suits their specific needs and helps them live a fulfilling and meaningful life. However, it is essential to remember that treatment is not a cure, and ongoing support and management strategies are crucial for long-term success.
The Role of Therapy in Managing Schizophrenia
Therapy plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of schizophrenia. While medication is often the primary treatment, therapy provides an additional layer of support and guidance for individuals with the condition. Through therapy, individuals with schizophrenia can work with mental health professionals to develop coping strategies, improve communication skills, and address the emotional and social challenges that accompany the disorder.
One important aspect of therapy for schizophrenia is the focus on cognitive-behavioral techniques. These techniques help individuals recognize and challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs, ultimately enhancing their ability to distinguish between reality and hallucinations or delusions. By targeting problematic thought patterns, therapy can assist individuals in reducing the severity and frequency of symptoms. Therapy also provides a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to explore their experiences, allowing them to gain a deeper understanding of their symptoms, emotions, and relationships.
The Impact of Stigma on Individuals with Schizophrenia
Individuals living with schizophrenia often face the additional burden of stigma, which can have a profound impact on their lives. Stigma refers to the negative attitudes, beliefs, and stereotypes associated with a particular condition or group of people. In the case of schizophrenia, this stigma can lead to social exclusion, discrimination, and limited opportunities for employment or relationships.
The impact of stigma on individuals with schizophrenia is far-reaching. It not only affects their mental and emotional well-being but also impedes their access to healthcare and support services. Stigmatizing attitudes can create barriers to seeking treatment, as individuals may fear judgment or rejection from others. This can result in delayed diagnosis and intervention, exacerbating the symptoms and reducing the chances of recovery.
Moreover, stigma can undermine the self-esteem and self-confidence of individuals with schizophrenia, making it challenging for them to engage in meaningful social interactions or pursue their goals and aspirations. The fear of being labeled as “crazy” or “dangerous” can isolate individuals, leading to feelings of loneliness and hopelessness. Additionally, the internalization of societal stigma can contribute to self-stigma, where individuals internalize negative beliefs about themselves, further diminishing their sense of self-worth.
It is imperative that society takes proactive measures to combat the stigma surrounding schizophrenia. Education and awareness campaigns can help dispel misconceptions and promote understanding of the condition. By fostering empathy and compassion, we can create an environment that supports individuals with schizophrenia in their journey towards recovery and inclusion. It is time to challenge the stereotypes and prejudices that perpetuate stigma, as everyone deserves a chance for a fulfilling and meaningful life, regardless of their mental health condition.
Supporting Individuals with Schizophrenia: Strategies for Family and Friends
When supporting individuals with schizophrenia, it is essential for family and friends to have a deep understanding of the challenges their loved ones face. This understanding can help them provide the necessary support and minimize the impact of symptoms on the individual’s daily life.
One strategy that can be beneficial is educating oneself about schizophrenia. By learning about the disorder, its symptoms, and treatment options, family and friends can gain valuable insights into the experiences of their loved ones. This knowledge can help them empathize with the challenges faced by individuals with schizophrenia and approach their care with compassion and understanding. Additionally, understanding the nature of the disorder can empower family and friends to advocate for their loved ones’ needs within healthcare systems and support networks. Education can be accessed through reputable sources such as mental health organizations, healthcare professionals, and support groups. It is important to seek information from credible sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
The Importance of Early Intervention in Schizophrenia
Early intervention is paramount in the management of schizophrenia. Research has shown that the sooner individuals receive appropriate treatment, the better the long-term outcomes are likely to be. Early intervention can significantly reduce the severity and duration of psychotic episodes, improve overall functioning, and enhance quality of life for those affected by this complex mental illness.
One of the main reasons why early intervention is crucial in schizophrenia is the potential for preventing or minimizing the negative impact on individuals’ lives. Studies have consistently demonstrated that delays in diagnosis and treatment can lead to an exacerbation of symptoms, increased hospitalizations, and a higher risk of relapse. By intervening early, healthcare professionals can provide timely support and implement effective treatment strategies to help individuals regain control over their lives and prevent further deterioration. Moreover, early intervention can also reduce the financial burden on healthcare systems and society as a whole, by decreasing the need for costly hospitalizations and long-term care.
Promising Research and Advances in Schizophrenia Treatment
In recent years, the field of schizophrenia research has witnessed significant advancements, offering hope for improved treatment outcomes for individuals living with this complex disorder. One area of promising research revolves around the development of new medications specifically designed to target the underlying neurobiological mechanisms of schizophrenia. These innovative drugs aim to minimize symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking, while also reducing the side effects commonly associated with traditional antipsychotics.
Additionally, advancements in brain imaging techniques have enabled researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the neuroanatomical and functional abnormalities present in individuals with schizophrenia. By exploring the intricate connections within the brain, scientists are uncovering valuable insights into the pathophysiology of the disorder. This enhanced knowledge has the potential to pave the way for more targeted interventions and personalized treatment approaches tailored to the unique needs of each individual. By harnessing the power of neuroimaging, researchers aim to develop more effective treatment strategies and gain valuable insights into the early detection and prevention of schizophrenia.
Addressing Co-Occurring Conditions in Schizophrenia
Individuals with schizophrenia often experience co-occurring conditions, which can significantly impact their overall well-being and quality of life. These conditions, also known as comorbidities, can include substance abuse disorders, depression, anxiety, and various physical health conditions. Addressing these co-occurring conditions is of utmost importance in the treatment and management of schizophrenia, as they can exacerbate symptoms and hinder the individual’s recovery process.
Research has shown that individuals with schizophrenia who also have co-occurring substance abuse disorders are at a higher risk of relapse, hospitalization, and poor treatment adherence. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to conduct comprehensive assessments to identify and address these substance abuse disorders in people with schizophrenia. Integrated treatment approaches that address both mental health and substance abuse simultaneously have been found to be most effective in reducing substance use, improving psychiatric symptoms, and enhancing overall functioning.
Furthermore, individuals with schizophrenia are more likely to experience depressive and anxiety symptoms compared to the general population. These co-occurring conditions can further impair social functioning, increase the risk of suicide, and decrease the individual’s overall quality of life. It is important for healthcare providers to assess and manage these symptoms through appropriate pharmacological and psychotherapeutic interventions.
The presence of physical health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity, is also prevalent among individuals with schizophrenia. These comorbidities often go untreated or undiagnosed, leading to significant health disparities and increased mortality rates. Healthcare professionals need to carefully monitor physical health parameters and provide necessary interventions, such as lifestyle modifications and medication management, to prevent and manage these conditions effectively.
In conclusion, addressing co-occurring conditions in individuals with schizophrenia is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes and improving their overall well-being. A comprehensive and integrated approach that considers the intricate relationship between these conditions is essential in providing effective care. By recognizing and addressing comorbidities, healthcare professionals can help individuals with schizophrenia achieve better stability, enhance their quality of life, and promote long-term recovery.
Enhancing Quality of Life for Individuals Living with Schizophrenia
People living with schizophrenia often face significant challenges that can impact their quality of life. However, there are ways to enhance their overall well-being and help them lead fulfilling lives. One crucial aspect is to provide a supportive and understanding environment. Creating a safe and inclusive space where individuals with schizophrenia feel accepted and valued can greatly contribute to their overall mental health. This can be achieved through education and awareness programs that aim to reduce the stigma surrounding schizophrenia and promote empathy and compassion.
In addition to fostering a supportive environment, it is essential to prioritize the physical health of individuals with schizophrenia. Encouraging regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and ensuring access to proper healthcare can significantly improve their overall well-being. Research has shown that physical activity is not only beneficial for physical health but can also have positive effects on mood and cognition. By incorporating exercise into their routine, individuals with schizophrenia can experience improved sleep patterns, reduced symptoms of depression, and enhanced cognitive function.
It is also crucial to address the social and emotional needs of individuals with schizophrenia. Engaging in meaningful social interactions, participating in support groups, and connecting with peers who share similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation. It is important to recognize that relationships may play a vital role in the recovery process and can help individuals maintain a sense of purpose and fulfillment. By fostering social connections and promoting community involvement, we can help enhance the quality of life for individuals living with schizophrenia.
What are the early warning signs and symptoms of schizophrenia?
Early warning signs of schizophrenia may include social withdrawal, lack of motivation, changes in sleep patterns, difficulty concentrating, and experiencing hallucinations or delusions.
How is schizophrenia diagnosed?
The diagnosis of schizophrenia is typically made by a mental health professional through a comprehensive assessment that includes a review of symptoms, medical history, and possibly psychological testing.
What are the treatment options for schizophrenia?
Treatment options for schizophrenia often include a combination of antipsychotic medications, counseling or therapy, and support services. These treatments aim to reduce symptoms, prevent relapses, and improve overall quality of life.
How does therapy help in managing schizophrenia?
Therapy can play a crucial role in managing schizophrenia by providing individuals with coping strategies, helping them understand their symptoms, promoting medication adherence, and improving social and occupational functioning.
How does stigma impact individuals with schizophrenia?
Stigma surrounding schizophrenia can lead to social isolation, discrimination, and limited access to resources and opportunities. It can negatively affect self-esteem, treatment adherence, and overall quality of life for individuals living with the condition.
What can family and friends do to support individuals with schizophrenia?
Family and friends can support individuals with schizophrenia by educating themselves about the condition, offering understanding and empathy, encouraging treatment compliance, and helping to create a supportive and inclusive environment.
Why is early intervention important in schizophrenia?
Early intervention in schizophrenia can lead to better long-term outcomes and improved quality of life. It allows for timely treatment, reduces the risk of relapse, and helps individuals maintain social relationships, work, and engage in meaningful activities.
Are there any promising research and advances in schizophrenia treatment?
Yes, ongoing research is exploring new treatment approaches for schizophrenia, including targeted therapies, cognitive remediation, and psychosocial interventions. These advancements aim to improve symptom management and enhance overall well-being.
How are co-occurring conditions addressed in schizophrenia?
Co-occurring conditions, such as substance abuse or anxiety disorders, are often addressed through integrated treatment approaches that target both schizophrenia symptoms and the associated condition. This may involve a combination of medication, therapy, and support services.
What strategies can enhance the quality of life for individuals living with schizophrenia?
Strategies to enhance the quality of life for individuals with schizophrenia may include a combination of medication adherence, regular therapy or counseling, support from loved ones, engagement in meaningful activities, and self-care practices to promote overall well-being.






