The Side Effects of Medications on Your Libido and How to Avoid Them
Understanding the Impact of Medications on Sexual Desire

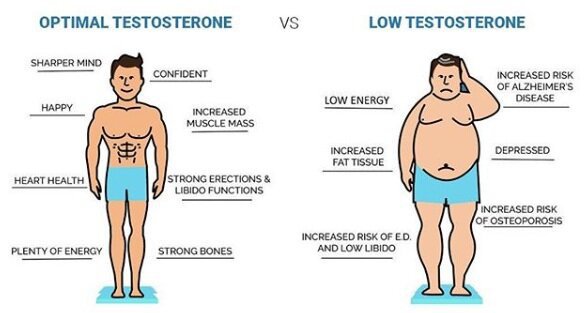
Medications play a crucial role in managing a wide array of health conditions, ranging from chronic illnesses to mental health disorders. While these medications are designed to improve overall well-being, it is important to understand that they can also have an impact on sexual desire. Sexual desire, also known as libido, refers to the individual’s interest in engaging in sexual activity. Certain medications, however, can interfere with this natural process and lead to changes in sexual desire, arousal, and overall sexual satisfaction.
There are different mechanisms through which medications can affect sexual desire. Some medications directly affect hormone levels, such as certain contraceptive pills or medications used in hormone therapy. Others may exert their influence on the central nervous system, interfering with the brain’s neurotransmitters and potentially affecting sexual functioning. Additionally, medications that target specific health conditions, such as antidepressants or blood pressure medications, can also have indirect effects on sexual desire. Understanding these mechanisms is important in order to better inform patients and healthcare providers about potential medication-induced changes in sexual desire and to explore strategies for managing such side effects.
Recognizing Common Medications That Can Affect Libido
Many medications can have an impact on sexual desire, leading to changes in libido for both men and women. It is important to be aware of the common medications that can affect libido in order to recognize and address any potential sexual side effects that may arise.
One type of medication that can affect libido is hormonal medications, such as those used for birth control or hormone replacement therapy. These medications work by altering hormone levels in the body, which can have unintended effects on sexual desire. Additionally, certain antidepressant medications, known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are often prescribed to manage depression or anxiety but can also lead to decreased libido as a side effect.
It is crucial for individuals to have a comprehensive understanding of the potential impact medications can have on sexual desire in order to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Identifying common medications that can affect libido is the first step in recognizing and addressing any potential concerns. With this knowledge, individuals can better manage their medication regimen and seek appropriate guidance from healthcare providers to minimize any negative impact on their sexual health.
Unveiling the Mechanisms Behind Medication-Induced Sexual Side Effects
Medication-induced sexual side effects can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall quality of life and intimate relationships. To better understand these side effects, it is essential to unveil the mechanisms through which certain medications can affect sexual desire.
One common mechanism is the alteration of neurotransmitter levels in the brain. Neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin play key roles in regulating sexual arousal and desire. Medications that target these neurotransmitters, such as antidepressants, can inadvertently disrupt the delicate balance, leading to decreased libido or difficulty achieving orgasm.
Additionally, hormonal medications can also contribute to sexual dysfunction. Hormones play a vital role in regulating sexual desire, and certain medications, such as oral contraceptive pills or hormone replacement therapy, can interfere with this delicate hormonal equilibrium. Fluctuations in estrogen and testosterone levels can directly impact libido and sexual functioning, making it important for individuals to be aware of potential side effects when taking such medications.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms behind medication-induced sexual side effects is crucial for healthcare providers to effectively manage and address these concerns. By recognizing the impact on neurotransmitters and hormonal balance, healthcare professionals can explore alternative medications or develop strategies to minimize these side effects. Seeking professional guidance is important for individuals experiencing medication-induced sexual side effects, as healthcare providers can offer personalized solutions and recommendations based on each individual’s unique medical history and needs.
The Role of Hormonal Medications in Sexual Dysfunction
Hormonal medications are commonly prescribed for various health conditions, including hormonal imbalances, birth control, and menopausal symptoms. While these medications can be highly beneficial in managing specific health issues, they may also have an impact on sexual functioning. It is crucial to understand the role of hormonal medications in sexual dysfunction, as it can have significant implications for individuals’ overall quality of life and relationships.
One primary way in which hormonal medications can affect sexual function is by altering hormone levels in the body. For example, certain hormonal contraceptives, such as combined oral contraceptives, work by suppressing ovulation and altering hormone levels to prevent pregnancy. However, this alteration in hormone levels can potentially lead to changes in sexual desire, arousal, and satisfaction. Similarly, hormonal medications used during menopause, such as hormone replacement therapy, aim to relieve symptoms like hot flashes and vaginal dryness. Although these medications can be effective in managing menopausal symptoms, they may also contribute to decreased sexual desire and difficulties with arousal.
It is important to note that the effect of hormonal medications on sexual function can vary widely from person to person. Factors such as the specific medication being used, individual physiology, and overall health can all influence how someone responds to hormonal treatment. If you are experiencing changes in sexual function while taking hormonal medications, it is crucial to discuss these concerns with your healthcare provider. They can provide further guidance and explore potential alternative treatment options if necessary.
Antidepressants and Their Impact on Sexual Functioning
Antidepressants are commonly prescribed medications used to treat various mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. While these medications can be highly effective in managing these conditions, one of the side effects that many individuals may experience is the impact on sexual functioning. It is estimated that up to 70% of people taking antidepressants may experience some form of sexual dysfunction.
There are different ways in which antidepressants can affect sexual functioning. These medications can potentially decrease libido, making individuals feel less interested or motivated to engage in sexual activity. They can also interfere with the physiological aspects of sexual function, such as arousal and orgasm. Some individuals may experience difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, a condition known as erectile dysfunction, while others may have delayed ejaculation or anorgasmia (inability to achieve orgasm). These sexual side effects can greatly affect an individual’s quality of life and may lead to decreased sexual satisfaction, relationship problems, and even treatment discontinuation.
While the exact mechanisms behind antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction are not fully understood, it is believed to involve the modulation of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly serotonin and dopamine. These neurotransmitters play crucial roles in regulating mood, emotions, and sexual functioning. By altering the balance of these neurotransmitters, antidepressants can inadvertently impact sexual desire and performance.
It is important to note that not all individuals taking antidepressants will experience sexual dysfunction. The occurrence and severity of these side effects can vary greatly among individuals and may depend on factors such as the specific medication used, the dosage, and individual characteristics. In some cases, switching to a different type of antidepressant or adjusting the dosage may help minimize these side effects. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to medication regimens.
In conclusion, antidepressants can have a significant impact on sexual functioning, with up to 70% of individuals experiencing some form of sexual dysfunction while taking these medications. It is important to remember that every individual may respond differently, and the occurrence and severity of these side effects can vary. If sexual dysfunction is affecting your quality of life or causing distress, it is essential to discuss these concerns with a healthcare provider who can provide guidance and explore potential strategies to manage these side effects.
Exploring the Effects of Blood Pressure Medications on Libido
Blood pressure medications are commonly used to treat hypertension and help manage cardiovascular health. While these medications play a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being, it is important to recognize that they may have potential side effects, including effects on sexual desire and functioning.
Certain types of blood pressure medications, such as beta blockers and diuretics, have been associated with a higher risk of sexual side effects. These effects can range from a decrease in sexual desire to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. It is thought that these medications may affect sexual function by altering blood flow and hormone levels in the body.
Several studies have explored the relationship between blood pressure medications and sexual health. A review published in the Journal of Hypertension found that beta blockers, such as propranolol and metoprolol, were more likely to cause sexual dysfunction compared to other classes of blood pressure medications. Another study in the Journal of Sexual Medicine reported that diuretics, specifically hydrochlorothiazide, were associated with an increased risk of erectile dysfunction.
It is important to note that not everyone taking blood pressure medications will experience sexual side effects. Additionally, the severity of these effects can vary among individuals. If you are concerned about the impact of blood pressure medication on your libido or sexual function, it is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider. They can assess your specific situation and discuss potential alternatives that may help minimize or manage any sexual side effects.
Understanding the Relationship Between Pain Medications and Sexual Desire
Pain medications play an essential role in managing various forms of pain, allowing individuals to find relief and improve their quality of life. However, it is important to recognize that certain pain medications can have an impact on sexual desire. This potential side effect can be attributed to the mechanisms of action of these medications and how they can affect the body’s hormonal balance.
One class of pain medications that can impact sexual desire is opioids. Opioids are commonly prescribed to alleviate moderate to severe pain. While they are effective in providing pain relief, opioids can also suppress the production of certain hormones, such as testosterone. Testosterone is vital for maintaining sexual desire in both men and women. Therefore, the reduction in testosterone levels caused by opioids can lead to a decrease in sexual desire and even sexual dysfunction. It is important for individuals taking opioids for pain management to be aware of this potential side effect and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
The Influence of Antipsychotic Medications on Sexual Health
Antipsychotic medications are commonly prescribed to individuals with mental health conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. While these medications can be effective in managing symptoms, they may also have a significant impact on sexual health. It is important for individuals and their healthcare providers to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss strategies for managing them.
One of the primary ways in which antipsychotic medications can affect sexual health is through their impact on neurotransmitters in the brain. These medications work by targeting receptors for dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood, motivation, and sexual desire. By blocking these receptors, antipsychotic medications can potentially decrease sexual desire and function. This effect can be particularly pronounced in men, who may experience difficulties with erectile dysfunction or delayed ejaculation. It is worth noting that individual responses to antipsychotic medications can vary, and not all individuals may experience these side effects.
(Sources:
1. Montejo, A. L., Llorca, G., Izquierdo, J. A., Rico-Villademoros, F., & De La Gandara, J. (2001). Incidence of sexual dysfunction associated with antidepressant agents: a prospective multicenter study of 1022 outpatients. Spanish Working Group for the Study of Psychotropic–Related Sexual Dysfunction. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 62(10), 10-21.
2. Murata, S., Motohashi, N., & Matsuzawa, D. (2017). Sexual dysfunction in patients with schizophrenia treated with typical antipsychotics, risperidone or olanzapine. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 31(4), 541-547.)
Examining the Effects of Anti-Anxiety Medications on Libido
Anti-anxiety medications, also known as anxiolytics, are commonly prescribed to manage anxiety disorders and related conditions. While these medications can be highly beneficial in reducing feelings of anxiety and promoting overall well-being, they may also have a notable impact on sexual desire and functioning. Understanding the effects of anti-anxiety medications on libido is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
One class of anti-anxiety medications, known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), is frequently prescribed for managing anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. While these medications are effective in alleviating anxiety symptoms, they have been associated with sexual side effects, including diminished libido and difficulty achieving orgasm. Research suggests that the mechanism behind these side effects may involve the modulation of serotonin levels in the brain, which can interfere with normal sexual response. It is important to note that not all individuals who take SSRIs will experience sexual side effects, and the severity of these effects can vary. Healthcare providers can offer guidance on potential side effects and discuss alternative treatment options if sexual concerns arise.
Another class of anti-anxiety medications, benzodiazepines, work by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. While benzodiazepines are not typically associated with sexual side effects, some individuals may experience decreased sexual desire or difficulties in arousal. These effects may be relatively rare and depend on individual factors and the specific medication prescribed. It is crucial for individuals experiencing changes in sexual functioning while taking anti-anxiety medications to discuss their concerns with a healthcare provider, who can assess the potential underlying causes and explore alternative treatment options if necessary.
In conclusion, it is evident that anti-anxiety medications can have an impact on libido and sexual functioning. The specific effects can vary depending on the type of medication prescribed and individual factors. Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is vital in managing any potential sexual side effects and finding the most suitable treatment approach for each individual. Further research and dialogue are needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind these effects and optimize the management of anxiety disorders while minimizing the impact on sexual health.
How Medications for Acid Reflux Can Impact Sexual Functioning
Acid reflux medications, commonly known as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), are commonly used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other acid-related conditions. While these medications can provide relief from acid reflux symptoms, it is important to be aware of their potential impact on sexual functioning.
Research suggests that taking PPIs over a prolonged period can increase the risk of sexual dysfunction, particularly in men. One study found that men who took PPIs for more than three months had a significantly higher likelihood of experiencing erectile dysfunction. Another study reported a link between PPI use and decreased libido in both men and women.
The exact mechanisms behind these effects are not yet fully understood, but researchers believe that PPIs may interfere with the production and bioavailability of nitric oxide, a molecule involved in sexual arousal. Additionally, PPIs can alter the balance of gut bacteria, which may contribute to sexual dysfunction.
It is important to discuss any concerns about medication-induced sexual side effects with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice and explore alternative treatment options if necessary. Additionally, implementing healthy lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and engaging in regular physical activity, may help to minimize the impact of medication on sexual functioning.
Shedding Light on the Connection Between Allergy Medications and Libido
Allergy medications are commonly prescribed to individuals who suffer from allergies caused by environmental factors such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. While these medications play a crucial role in alleviating allergy symptoms, it is important to understand the potential impact they may have on libido and sexual desire. Several studies have explored the connection between allergy medications and sexual health, shedding light on the mechanisms through which these medications can affect one’s libido.
Histamine is a key component in the body’s inflammatory response and is involved in allergic reactions. Antihistamine medications, commonly prescribed for allergy relief, work by blocking the effects of histamine. However, research suggests that these medications may also affect sexual desire and arousal. A study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine found that antihistamines can interfere with the release of key neurotransmitters involved in sexual arousal, leading to a decrease in sexual desire. It is important to note that not all antihistamines have the same impact on libido, and the severity of the side effect may vary between individuals. As always, discussing any concerns regarding medication-induced sexual side effects with your healthcare provider is essential for appropriate management.
• Antihistamine medications, commonly prescribed for allergy relief, can potentially impact libido and sexual desire.
• These medications work by blocking the effects of histamine, a key component in the body’s inflammatory response.
• Research suggests that antihistamines may interfere with the release of key neurotransmitters involved in sexual arousal.
• A study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine found a decrease in sexual desire associated with antihistamine use.
• Not all antihistamines have the same impact on libido, and individual experiences may vary.
• Discussing any concerns regarding medication-induced sexual side effects with a healthcare provider is important for appropriate management.
Managing Diabetes Medications and Their Impact on Sexual Desire
When it comes to managing diabetes, it is important to understand and address the potential impact that medications can have on sexual desire. Many diabetes medications, such as insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents, are known to affect sexual functioning in both men and women. This can include a decrease in sexual desire, difficulties with arousal and lubrication, as well as erectile dysfunction in men.
One of the key mechanisms behind these medication-induced sexual side effects is the effect that diabetes medications can have on blood flow and nerve function. High blood glucose levels, which are common in individuals with diabetes, can lead to damage to the blood vessels and nerves that are essential for normal sexual functioning. Additionally, certain diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas, have been found to directly affect hormone levels, further impacting sexual desire and performance.
In order to address these issues, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider. They can help to adjust your diabetes medications to find a balance between managing your blood sugar levels and minimizing the impact on your sexual desire. In some cases, alternative medications or treatments may be recommended, depending on your specific situation. It is also important to manage your diabetes through lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet. These measures can not only help to improve sexual functioning but also overall health and well-being.
Strategies for Minimizing Medication-Induced Sexual Side Effects
When it comes to managing medication-induced sexual side effects, there are several strategies that individuals can consider. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential, as they can provide personalized advice based on the specific medication being taken and the individual’s overall health. In some cases, adjusting the dosage or switching to an alternative medication with fewer sexual side effects may be an option. It is important to note that any changes to medication should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.
In addition to medication adjustments, lifestyle modifications can also play a role in minimizing sexual side effects. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can contribute to overall well-being and potentially alleviate some sexual disturbances. Maintaining open communication with a partner about any concerns or changes in sexual desire or functioning is also crucial. Together, individuals and their partners can explore different techniques and strategies to enhance intimacy and sexual satisfaction. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor who specializes in sexual health can provide additional guidance and resources for managing medication-induced sexual side effects.
Seeking Professional Guidance: When and How to Discuss Medication-Related Sexual Concerns with Your Healthcare Provider
It is crucial to seek professional guidance when experiencing medication-related sexual concerns, as healthcare providers can offer valuable insight and support. If you are experiencing changes in sexual desire or functioning while taking medication, it is essential to have an open and honest conversation with your doctor. By discussing your concerns, you can work together to find a solution that manages your health condition while minimizes the impact on your sexual well-being.
When approaching the topic with your healthcare provider, it is essential to maintain a professional and respectful tone. Remember that discussing sexual concerns is a normal part of healthcare, and your doctor is trained to address these issues. Start the conversation by clearly expressing your specific concerns and any changes you have noticed in your sexual desire or functioning. Providing detailed information will allow your healthcare provider to assess the situation thoroughly and provide appropriate recommendations. They may ask further questions about your medical history, current medications, and any other factors that could contribute to the sexual side effects you are experiencing.
How do medications impact sexual desire?
Medications can have various effects on sexual desire, including reducing libido or causing sexual dysfunction.
Which common medications can affect libido?
Some common medications that can affect libido include hormonal medications, antidepressants, blood pressure medications, pain medications, antipsychotic medications, anti-anxiety medications, medications for acid reflux, allergy medications, and diabetes medications.
What are the mechanisms behind medication-induced sexual side effects?
The mechanisms behind medication-induced sexual side effects can vary depending on the medication, but they often involve alterations in hormone levels, neurotransmitter imbalances, or changes in blood flow.
How do hormonal medications contribute to sexual dysfunction?
Hormonal medications, such as certain birth control methods or hormone replacement therapy, can affect sexual desire by altering hormone levels in the body.
What impact do antidepressants have on sexual functioning?
Antidepressants can often cause sexual side effects, such as decreased libido, difficulty reaching orgasm, or erectile dysfunction.
Do blood pressure medications affect libido?
Yes, blood pressure medications can sometimes affect libido and sexual functioning, although not all medications in this category have the same impact.
Is there a link between pain medications and sexual desire?
Yes, certain pain medications can affect sexual desire and performance, potentially due to their impact on the central nervous system.
How do antipsychotic medications influence sexual health?
Antipsychotic medications can affect sexual health by reducing sexual desire, causing erectile dysfunction, or altering hormone levels.
Can anti-anxiety medications impact libido?
Yes, some anti-anxiety medications can have sexual side effects, such as decreased libido or difficulty achieving sexual satisfaction.
How do medications for acid reflux affect sexual functioning?
Medications for acid reflux, such as proton pump inhibitors, have been associated with sexual side effects, although the exact mechanisms are not yet fully understood.
Is there a connection between allergy medications and libido?
Some allergy medications, particularly certain antihistamines, may cause temporary or long-term sexual side effects, such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction.
How do diabetes medications impact sexual desire?
Diabetes medications can sometimes affect sexual desire due to their influence on blood sugar levels, hormone regulation, or blood flow.
What strategies can be used to minimize medication-induced sexual side effects?
Strategies for minimizing medication-induced sexual side effects may include adjusting the dosage, switching to a different medication, adding a medication to counteract the side effects, or employing non-pharmacological interventions.
When and how should I discuss medication-related sexual concerns with my healthcare provider?
It is important to discuss medication-related sexual concerns with your healthcare provider as soon as you notice any issues. Schedule an appointment to openly discuss the concerns, provide a detailed account of your symptoms, and ask questions about potential solutions or alternatives to the current medication.