The Surprising Male and Female Infertility Facts You Need To Know

Table of Contents
Understanding the Factors Behind Infertility

Infertility is a complex condition that affects a significant number of men and women worldwide. While there are numerous factors at play, understanding the underlying causes can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their reproductive health. In men, common causes of infertility include low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and structural abnormalities in the reproductive organs. Additionally, factors such as chronic illnesses, hormonal imbalances, and genetic disorders can also contribute to male infertility.
On the other hand, female infertility can be attributed to a range of factors, including hormonal imbalances, structural abnormalities in the reproductive organs, and ovulation disorders. Some women may also experience infertility due to conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis. Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals and toxins, as well as lifestyle factors like excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, can further impact fertility in both men and women. By assessing these underlying factors, healthcare professionals can provide tailored treatment options to help couples achieve their goal of starting a family.
The Prevalence of Infertility in Men and Women

Infertility is a widespread issue that affects both men and women around the world. According to research, approximately 10-15% of couples struggle with infertility, with nearly half of the cases attributed to male factors. In men, infertility can result from various causes such as low sperm count, abnormal sperm morphology, and impaired sperm motility. On the other hand, female infertility can be caused by factors like ovulatory disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, or hormonal imbalances. It is important to note that infertility can affect individuals regardless of age, socioeconomic status, or lifestyle choices. Understanding the prevalence of infertility in both men and women is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and providing support to those who are struggling to conceive.
It is worth mentioning that the prevalence of infertility varies across different regions and populations. Research has shown that infertility rates tend to be higher in developed countries compared to developing nations. This can be attributed to factors such as the delay in childbearing, higher stress levels, and the increasing age of couples when they decide to start a family. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to environmental toxins have also been linked to increased infertility rates. It is therefore important for individuals and couples to be aware of these factors and take proactive steps to improve their reproductive health.
While infertility can be a challenging and emotional journey for many couples, it is essential to seek support and explore treatment options. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a fertility specialist or a gynecologist, is the first step in diagnosing the underlying causes of infertility. They can guide individuals through various diagnostic tests, including semen analysis, hormonal evaluations, and ultrasound examinations, to identify any potential issues. It is important to understand that infertility is a medical condition that can often be treated with the help of assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), or hormone therapy. Seeking support from support groups and counseling services can also provide emotional support throughout the infertility journey.
The Impact of Age on Fertility in Men and Women

Age is an important factor when it comes to fertility, both in men and women. As individuals age, the chances of conceiving decrease, and the risk of certain fertility issues increases. In women, the quality and quantity of eggs decline with age, leading to difficulties in getting pregnant. Research suggests that a woman’s fertility starts to decline significantly after the age of 35. This decline becomes even more pronounced after the age of 40.
In men, age also plays a role in fertility. While men continue to produce sperm throughout their lifetime, the quality of the sperm may diminish as they age. Studies have shown that older men may have a higher incidence of genetic abnormalities in their sperm, which can increase the risk of miscarriages and certain birth defects. It is important for both men and women to be aware of the impact of age on fertility and to consider family planning options accordingly.
Common Causes of Male Infertility
Male infertility is a common issue that affects many couples trying to conceive. It is estimated that approximately 15% of couples will experience difficulty in conceiving, with about half of these cases attributed to male factor infertility. While there can be various factors contributing to male infertility, let us delve deeper into some common causes.
One of the primary causes of male infertility is a low sperm count, also known as oligospermia. This refers to a reduced number of sperm cells in the ejaculate, which ultimately decreases the chances of fertilization. Several factors can contribute to a low sperm count, including hormonal imbalances, genetic abnormalities, varicocele (enlarged veins within the scrotum), and infections such as epididymitis or orchitis. Additionally, certain lifestyle factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, smoking, and exposure to toxins or pollutants can also contribute to a decrease in sperm count.
Here’s a table summarizing common causes of male infertility:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Sperm Count (Oligospermia) | Low sperm count, or oligospermia, is a common cause of male infertility characterized by a lower-than-normal concentration of sperm in the ejaculate. Factors contributing to low sperm count include hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum), infections, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to toxins or environmental pollutants. |
| Poor Sperm Motility (Asthenospermia) | Poor sperm motility, or asthenospermia, refers to reduced sperm movement or forward progression, which hinders their ability to reach and fertilize the egg. Causes of poor sperm motility may include genetic abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, infections, varicocele, heat exposure (such as hot tubs or saunas), and lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, or excessive alcohol intake. |
| Abnormal Sperm Morphology (Teratospermia) | Abnormal sperm morphology, or teratospermia, involves sperm with abnormal shapes or sizes, which may affect their ability to fertilize an egg. Causes of teratospermia include genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, varicocele, infections, exposure to environmental toxins, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or drug use. |
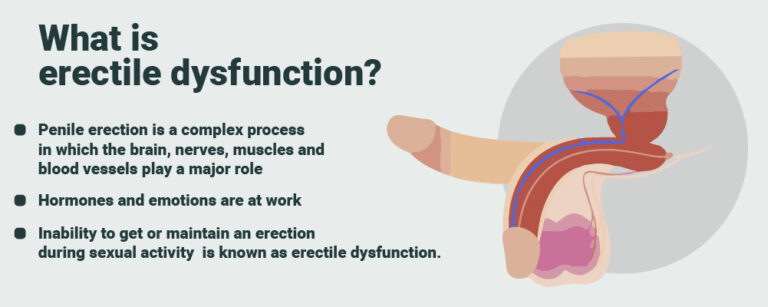
| Erectile Dysfunction | Erectile dysfunction (ED) refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. While ED itself does not directly cause infertility, it can affect a man’s ability to engage in sexual intercourse and ejaculate semen into the female reproductive tract, thereby reducing the chances of conception. Common causes of erectile dysfunction include vascular issues, nerve damage, hormonal imbalances, psychological factors, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease. |
| Ejaculatory Disorders | Ejaculatory disorders such as retrograde ejaculation, premature ejaculation, or anejaculation can interfere with the release of semen during ejaculation, leading to infertility. Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen enters the bladder instead of being expelled through the urethra, while premature ejaculation involves ejaculating before or shortly after penetration. Anejaculation refers to the absence of ejaculation despite sexual stimulation. Causes of ejaculatory disorders may include nerve damage, hormonal imbalances, medications, psychological factors, or surgery. |
| Obstructions in the Reproductive Tract | Obstructions in the male reproductive tract, such as blockages in the vas deferens, epididymis, or ejaculatory ducts, can prevent the transport of sperm from the testes to the urethra for ejaculation. Obstructions may result from congenital anomalies, infections, scarring due to surgery or trauma, or conditions such as cystic fibrosis. |
| Hormonal Imbalances | Hormonal imbalances involving disruptions in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis can affect sperm production and function, leading to infertility. Common hormonal disorders affecting male fertility include hypogonadism (low testosterone levels), hyperprolactinemia, thyroid disorders, adrenal insufficiency, and abnormalities in other hormone-producing glands. Hormonal imbalances may result from genetic factors, tumors, medications, or systemic diseases. |
| Genetic Factors | Genetic abnormalities or mutations can contribute to male infertility by affecting sperm production, function, or reproductive anatomy. Genetic causes of male infertility may include chromosomal abnormalities (such as Klinefelter syndrome or Y chromosome deletions), gene mutations associated with sperm production or function, or inherited conditions affecting reproductive development or function. Genetic testing may be recommended to identify underlying genetic factors contributing to infertility. |
Surprising Lifestyle Factors That Affect Male Fertility
When it comes to male fertility, there are several lifestyle factors that can have surprising effects on reproductive health. One such factor is excessive alcohol consumption. While the occasional drink may not cause major harm, excessive alcohol intake can lead to decreased sperm quality and production. Studies have shown that heavy drinking can disrupt hormone levels, reduce sperm count, and even cause abnormal sperm shape and movement. Therefore, it is advised for men who are trying to conceive to limit their alcohol consumption or consider abstaining altogether.
Another surprising lifestyle factor that can impact male fertility is exposure to heat. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as through sitting for long periods in hot tubs or saunas, can raise scrotal temperatures and negatively affect sperm production. Additionally, wearing tight-fitting underwear or pants can also increase scrotal temperatures and impair sperm quality. It is recommended for men to opt for loose-fitting clothing and to avoid excessive heat exposure to promote optimal reproductive health.
Understanding these surprising lifestyle factors and their impact on male fertility can help individuals make informed decisions and take proactive steps towards improving their reproductive health. By limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding excessive heat exposure, men can optimize their chances of successful conception. Further research and studies are needed to delve deeper into these factors and their mechanisms of action, but it is essential to explore all possible avenues when it comes to fertility and reproductive well-being.
Female Infertility: An Overview of Potential Causes
Female infertility is a complex condition with a variety of potential causes. One common cause is age-related decline in fertility. As women age, the quantity and quality of their eggs decreases, making it more difficult to conceive. This decline begins in the late 20s and becomes more pronounced after the age of 35. Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to female infertility. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders can disrupt the normal ovulation process, leading to difficulty in conceiving. Additionally, structural abnormalities in the reproductive organs, such as blocked fallopian tubes or uterine abnormalities, can hinder the implantation of a fertilized egg.
In addition to these factors, certain lifestyle choices can also impact female fertility. Chronic stress has been linked to infertility, as it can disrupt the balance of hormones necessary for ovulation and implantation. Environmental factors, such as exposure to chemicals and toxins, can also have a negative effect on reproductive health. These factors, combined with other causes such as genetic conditions, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications, contribute to the complexity of female infertility. Understanding these potential causes is essential in order to develop effective treatment strategies and provide support to women and couples struggling with infertility.
The Role of Hormonal Imbalances in Female Infertility
Hormonal imbalances can play a significant role in female infertility. The reproductive system in women is intricately regulated by a complex interplay of hormones, and any disruption in this delicate balance can have profound effects on fertility.
One common hormonal imbalance that can affect fertility is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is characterized by an excess production of androgens, which are male hormones, in women. This hormonal imbalance can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation (lack of ovulation), and the formation of ovarian cysts. It is estimated that PCOS affects approximately 5-10% of women of childbearing age, and it is a leading cause of female infertility.
Another hormonal imbalance that can impact fertility is thyroid dysfunction. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various metabolic processes in the body, including the menstrual cycle and ovulation. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can disrupt the normal functioning of the reproductive system, leading to difficulties in conceiving. Thyroid disorders are relatively common, affecting around 5-10% of women, and it is important to diagnose and manage them appropriately to optimize fertility.
It is worth noting that hormonal imbalances can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, certain medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. In some cases, addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance through medication or lifestyle modifications can improve fertility outcomes. Therefore, it is crucial for women experiencing infertility to undergo thorough hormonal evaluations to identify any imbalances and receive appropriate treatment.
• Hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid dysfunction, can significantly impact female fertility.
• PCOS is characterized by excess production of male hormones in women, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation, and ovarian cysts.
• Approximately 5-10% of women of childbearing age are affected by PCOS, making it a prevalent cause of infertility.
• Thyroid dysfunction, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can disrupt the reproductive system’s normal functioning and hinder conception.
• Around 5-10% of women experience thyroid disorders that may affect their fertility.
• Hormonal imbalances can be caused by various factors like genetics, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices.
• Addressing underlying hormonal imbalances through medication or lifestyle modifications may improve fertility outcomes for some individuals.
• Thorough hormonal evaluations are crucial for identifying any imbalances and receiving appropriate treatment when experiencing infertility.
Surprising Environmental Factors That Can Affect Female Fertility
Environmental factors play a significant role in female fertility, and some of the surprising elements in our surroundings can have detrimental effects on reproductive health. One such factor is exposure to endocrine disruptors, which are chemicals that interfere with the hormonal balance in the body. These substances can be found in everyday products such as plastics, cosmetics, and cleaning agents. Research has shown that exposure to endocrine disruptors can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, hormonal imbalances, and even impaired embryo development. Therefore, it is crucial for women to be aware of the products they use and opt for those that are free from such harmful chemicals.
Another surprising environmental factor that can affect female fertility is air pollution. Studies have found that high levels of air pollution, particularly particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, can have adverse effects on women’s reproductive health. The harmful pollutants in the air can impact ovarian function, disrupt hormone levels, and even increase the risk of miscarriage. It is essential for women to limit their exposure to polluted environments, especially during preconception and pregnancy periods. This may include avoiding areas with heavy traffic or industrial sites, using air purifiers at home, and engaging in outdoor activities in cleaner, less polluted areas.
In conclusion, women should be conscious of the impact that environmental factors can have on their fertility. By avoiding exposure to endocrine disruptors and reducing their exposure to air pollution, women can take proactive steps to protect their reproductive health. Understanding and addressing these surprising environmental factors can contribute to positive fertility outcomes.
Exploring the Link Between Stress and Infertility in Both Genders
Stress is a common aspect of modern life, affecting individuals of all genders and ages. But recent research suggests that stress may also play a significant role in infertility. While the exact mechanisms behind this link are not fully understood, several theories have been proposed.
For both men and women, stress can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones involved in reproduction. Chronic stress may lead to an increase in stress hormones such as cortisol, which can interfere with the production of vital reproductive hormones. Additionally, stress can have a negative impact on sperm quality in males, affecting sperm count, motility, and morphology. In females, stress may disrupt the delicate hormonal cycles necessary for ovulation and successful conception.
Furthermore, stress can also affect the way individuals cope with infertility treatments. The emotional and psychological toll of infertility can be immense, leading to increased stress levels and potentially impacting treatment outcomes. Stress may interfere with medication adherence, disrupt sleep patterns, and even contribute to depression or anxiety, all of which can further complicate the fertility journey.
While further research is needed to fully understand the intricate relationship between stress and infertility, it is clear that stress management should be an integral part of any comprehensive fertility treatment plan. By addressing stress using techniques such as meditation, exercise, counseling, and lifestyle modifications, individuals and couples can potentially improve their chances of conception. Seeking support and exploring stress reduction strategies may not only enhance overall well-being but also positively contribute to reproductive health.
The Connection Between Obesity and Infertility
Obesity is a growing concern worldwide, with its prevalence reaching epidemic proportions. While its negative impact on various aspects of health is well-documented, recent research has shed light on the connection between obesity and infertility. Both in men and women, obesity has been found to be a significant risk factor for fertility issues.
In men, obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances, such as decreased testosterone levels and increased estrogen production. These hormonal disturbances can impair sperm production, motility, and morphology, ultimately affecting male fertility. Furthermore, excess body fat can also lead to higher scrotal temperatures, which can further hinder sperm production and function. Several studies have shown a clear association between obesity and reduced sperm quality and quantity, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for optimal reproductive health.
In women, obesity has been linked to various reproductive complications, including menstrual irregularities, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and infertility. Research has indicated that excess adipose tissue can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance necessary for regular ovulation. Obesity is also associated with insulin resistance, which can further exacerbate hormonal imbalances and interfere with the reproductive process. Additionally, obese women may experience difficulties in conceiving due to impaired implantation of the fertilized embryo in the uterine lining. Understanding and addressing the impact of obesity on female fertility is crucial for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive.
While the connection between obesity and infertility is well-established, it’s important to note that weight loss and adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly improve fertility outcomes. By making dietary modifications, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking medical guidance, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving a healthy weight and enhancing their fertility potential. Exploring the link between obesity and infertility not only underscores the importance of weight management, but also highlights the need for comprehensive support and treatment options for individuals and couples struggling with infertility.
The Surprising Impact of Diet and Nutrition on Fertility
Maintaining a healthy diet and nutrition is crucial for overall well-being, and it may come as a surprise that it also plays a significant role in fertility. Research has shown that certain dietary choices can affect both male and female reproductive health, potentially influencing the chances of conceiving.
For women, a balanced diet rich in nutrients such as folic acid, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids is particularly important for optimal fertility. Studies have suggested that a deficiency in these nutrients may lead to menstrual irregularities and ovulatory dysfunction, making it more difficult to get pregnant. On the other hand, consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugar has been associated with an increased risk of infertility in women. This is thought to occur due to the disruption of insulin and hormone levels, which can negatively affect reproductive function. To enhance fertility, it is recommended that women focus on consuming a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
In men, diet and nutrition also play a crucial role in reproductive health. Certain nutrients have been found to support the production of healthy sperm, such as antioxidants, zinc, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids. A deficiency in these nutrients may lead to impaired sperm quality and quantity. On the other hand, excessive consumption of processed meats, trans fats, and alcohol has been associated with decreased sperm quality. Therefore, men looking to optimize fertility should aim to include sources of these beneficial nutrients in their diet, while also avoiding or moderating intake of substances that have been linked to reduced sperm health.
The Role of Exercise and Physical Activity in Fertility
Physical exercise and regular physical activity play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. When it comes to fertility, both men and women can benefit from incorporating exercise into their lifestyle. Research has shown that engaging in moderate to vigorous physical activity can enhance fertility and increase the chances of conception.
For women, exercise can help regulate hormonal levels, improve blood circulation to the reproductive organs, and promote a healthy body weight, all of which are important factors for fertility. Regular exercise can also help reduce stress levels, which can have a negative impact on fertility. However, it is important to note that excessive exercise or intense training, especially in women with low body fat percentage, may lead to irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances, which can affect fertility.
In men, exercise has been found to improve sperm quality and quantity. Regular physical activity helps increase blood flow to the testicles, which can enhance sperm production. Additionally, exercise can help maintain a healthy body weight and reduce the risk of conditions such as obesity and metabolic syndrome, which have been linked to male infertility. However, it is important for men to avoid excessive exercise or prolonged exposure to high temperatures, as these factors can negatively affect sperm production.
While exercise can have positive effects on fertility, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or altering any exercise routine, especially for individuals with underlying medical conditions or fertility concerns. Additionally, it is recommended to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet along with regular physical activity, as proper nutrition is vital for reproductive health.
Understanding the Psychological Effects of Infertility
Individuals and couples who are struggling with infertility not only face physical challenges but also bear the weight of profound psychological effects. The emotional toll of infertility can be devastating, affecting various aspects of a person’s life including self-esteem, relationships, and overall well-being. The inability to conceive can often lead to feelings of sadness, grief, anxiety, and even depression.
One of the most common psychological impacts of infertility is the sense of loss and grief experienced by individuals as they face the realization that they may never be able to have biological children. This grief can manifest in various ways, including feelings of emptiness, guilt, and a sense of failure. Couples may also find themselves facing social pressure and judgment from their families, friends, and society, which further exacerbates the emotional burden they carry.
In addition to the grief and societal pressure, individuals dealing with infertility may also experience strain on their interpersonal relationships. The stress and emotional rollercoaster of infertility can put a strain on the dynamics between partners and lead to feelings of frustration, blame, and guilt. Intimate relationships may become strained as sex becomes associated solely with procreation and loses its previous emotional intimacy. This can create a cycle of stress and disappointment, further impacting the emotional well-being of both individuals in the relationship.
It is vital to acknowledge and address these psychological effects of infertility in order to support individuals and couples through their fertility journey. Providing access to professional counseling and support groups can be instrumental in helping individuals navigate their emotions during this challenging time. By creating a safe and understanding environment, healthcare professionals and support networks can help individuals and couples develop coping mechanisms, enhance their emotional resilience, and find ways to maintain a positive outlook and quality of life despite the challenges they face.
Seeking Support and Treatment Options for Infertility
When faced with the challenges of infertility, seeking emotional and professional support is crucial. Dealing with infertility can be an overwhelming and emotional journey, and having a strong support system can provide comfort and guidance during this time. Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can offer a sense of understanding and validation, reducing feelings of isolation. Support groups, either in-person or online, can provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and receive empathetic support.
In addition to emotional support, seeking professional assistance is vital for identifying and treating the underlying causes of infertility. Consulting with a reproductive specialist or fertility doctor can help assess the individual’s reproductive health and provide tailored treatment options. These specialists have the knowledge and expertise to conduct comprehensive evaluations, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate interventions. By collaborating with a medical professional, individuals can access a wide range of treatment options that may include medication, surgery, or assisted reproductive technologies like intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF). Through proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, individuals and couples can increase their chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
What are the common causes of male infertility?
Male infertility can be caused by factors such as low sperm count, poor sperm quality, hormonal imbalances, varicocele, and genetic disorders.
What lifestyle factors can affect male fertility?
Surprisingly, factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, obesity, and exposure to certain environmental toxins can have a negative impact on male fertility.
What are some potential causes of female infertility?
Female infertility can be caused by conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes, hormonal imbalances, and age-related decline in egg quality.
How do hormonal imbalances contribute to female infertility?
Hormonal imbalances, such as irregular menstrual cycles or problems with ovulation, can disrupt the normal reproductive process and lead to difficulties in conceiving.
Are there any surprising environmental factors that can affect female fertility?
Yes, exposure to certain chemicals found in everyday products like plastics, pesticides, and cosmetics, as well as high levels of air pollution, have been linked to decreased fertility in women.
Is there a connection between stress and infertility?
Yes, stress can have a negative impact on both male and female fertility. Chronic stress can affect hormone levels, disrupt ovulation and sperm production, and decrease the chances of conceiving.
How does obesity affect fertility?
Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and inflammation, all of which can interfere with normal reproductive function and decrease fertility in both men and women.
Can diet and nutrition affect fertility?
Yes, a healthy diet and proper nutrition are essential for reproductive health. Certain nutrients, like folic acid, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids, can improve fertility in both men and women.
Does exercise play a role in fertility?
Yes, regular physical activity is important for maintaining a healthy weight and promoting overall well-being, which can positively impact fertility. However, excessive exercise or intense training can have a negative effect on fertility.
What are the psychological effects of infertility?
Infertility can cause significant emotional distress, including feelings of sadness, anxiety, guilt, and frustration. It can also strain relationships and lead to a decrease in self-esteem.
What treatment options are available for infertility?
Treatment options for infertility vary depending on the underlying cause but may include lifestyle changes, medication, surgery, assisted reproductive techniques (such as in vitro fertilization), and counseling or support groups.