From Diagnosis to Recovery: How to Navigate Your Prostate Cancer Journey with Confidence
Understanding Prostate Cancer: Types, Causes, and Risk Factors

Prostate cancer is a complex disease that affects the male reproductive system. It is important to understand the different types, causes, and risk factors associated with this condition in order to raise awareness and promote early detection.
Types of prostate cancer can be classified based on the grade and stage of the disease. The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which originates in the glandular cells of the prostate. Other less common types include small cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors. Understanding the specific type of prostate cancer is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Several factors can contribute to the development of prostate cancer. Age is considered a major risk factor, with the majority of cases occurring in men over the age of 50. Family history and genetics also play a significant role, as individuals with a family history of prostate cancer are at a higher risk of developing the disease. Additionally, race and ethnicity can influence the likelihood of prostate cancer, with African-American men having a higher incidence rate compared to other ethnic groups. Further research is needed to understand the exact causes of prostate cancer and to identify additional risk factors associated with this condition.
In conclusion, gaining a comprehensive understanding of prostate cancer is essential for early detection and effective treatment. By recognizing the different types, causes, and risk factors, healthcare professionals can develop personalized approaches to managing this disease. It is important for men to be aware of the signs and symptoms of prostate cancer and to consult with a healthcare professional if any concerns arise.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men, and recognizing its signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. However, it is important to note that symptoms may vary from person to person, and some men may not experience any symptoms at all in the early stages of the disease.
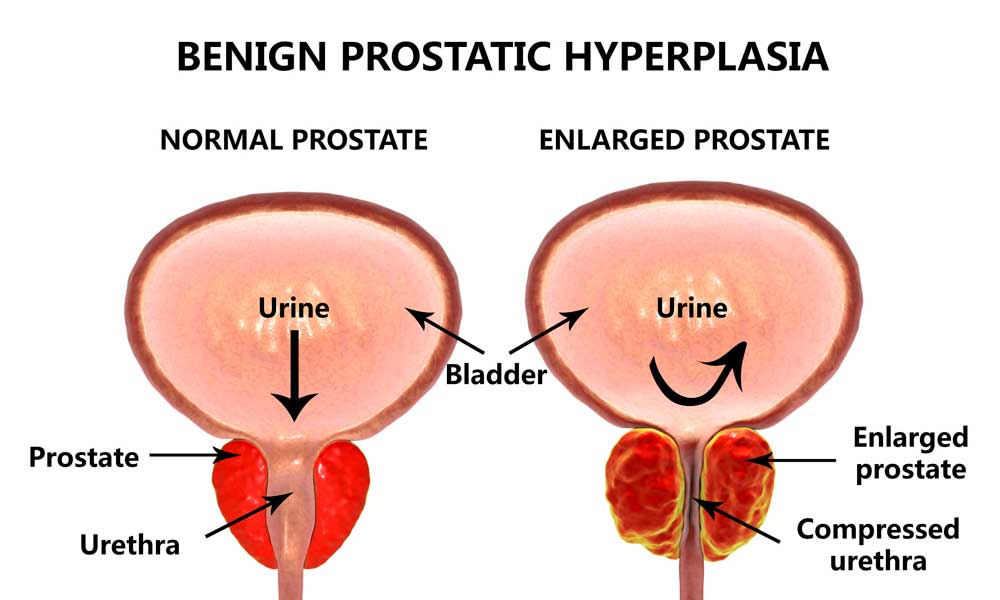
One of the most common signs of prostate cancer is changes in urinary frequency and flow. Men may experience increased frequency of urination, especially during the night. They may also have trouble starting and stopping the urine stream or have a weak urine flow. Additionally, some men may notice blood in their urine or semen, which can be a cause for concern. It is important to remember that these symptoms can also be associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a non-cancerous condition that affects the prostate gland. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Seeking Medical Help: When to Consult a Healthcare Professional

Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of prostate cancer is crucial in ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment. While some symptoms may be non-specific and can be indicative of other conditions, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
1. Urinary Changes: Increased frequency of urination, particularly at night, weak urine flow, difficulty initiating or stopping urine stream, or a sense of incomplete emptying of the bladder may be signs of prostate cancer. These symptoms can also be associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), but a medical assessment is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
2. Blood in Urine or Semen: The presence of blood in urine or semen can be alarming and should never be ignored. While it may not always be indicative of prostate cancer, it is vital to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation to rule out any serious conditions.
Remember, these symptoms can also be associated with non-cancerous conditions, such as prostatitis or urinary tract infections. However, it is crucial not to dismiss any unusual changes and seek medical help to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Getting a Proper Diagnosis: Tests and Procedures
During the process of diagnosing prostate cancer, various tests and procedures are utilized to accurately assess the presence and extent of the disease. One of the initial steps is a digital rectal exam (DRE), where the doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to examine the prostate for any abnormalities in size, shape, or texture. While this may cause slight discomfort, it is a relatively quick and straightforward procedure.
In addition to the DRE, another common test used for prostate cancer diagnosis is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. This test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland, in the blood. Elevated PSA levels may indicate the presence of prostate cancer, but further investigation is required to confirm the diagnosis. It is important to note that while the PSA test is a valuable tool, it is not specific to prostate cancer and can be influenced by various factors, such as age and certain medical conditions. Therefore, additional tests may be necessary to determine the cause of elevated PSA levels and to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer: Exploring the Possibilities
Prostate cancer is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer in men, and understanding the treatment options available is crucial for patients and their loved ones. When it comes to treating prostate cancer, there are several possibilities to explore, each with its own benefits and considerations.
One common treatment option is surgery, which involves removing the prostate gland. This procedure, known as a radical prostatectomy, can be performed using different techniques such as open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or robot-assisted surgery. Surgery is often recommended for patients with localized prostate cancer, where the cancer has not spread beyond the prostate gland. However, it’s important to note that surgery may carry risks and potential side effects, such as erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence.
Another treatment option for prostate cancer is radiation therapy, which uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. This non-invasive approach can be administered externally through a machine or internally using radioactive implants. Radiation therapy is often considered for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery or prefer a less invasive treatment option. However, it’s important to discuss the potential side effects of radiation therapy, such as fatigue and urinary problems, with your healthcare professional.
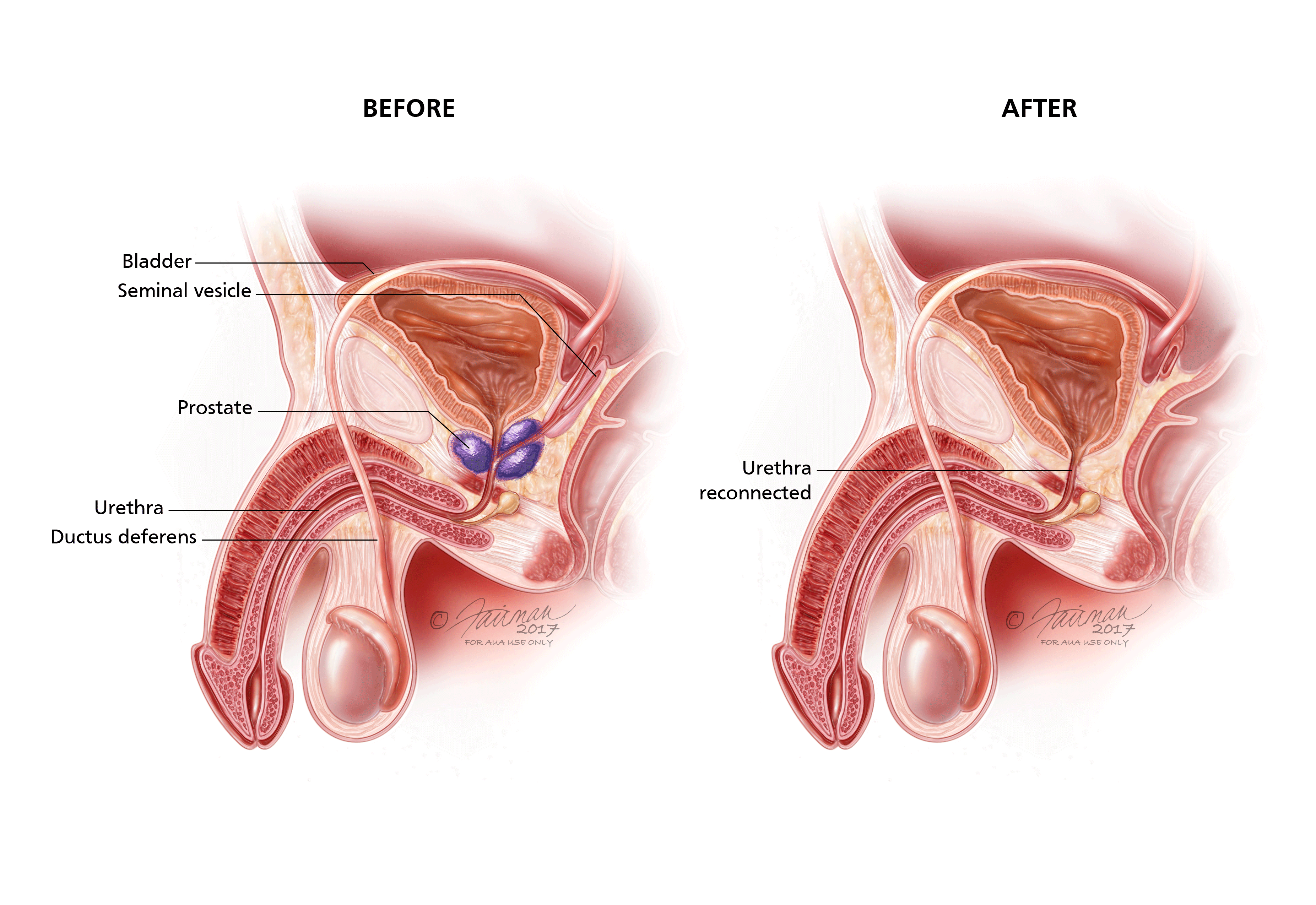
Surgery as a Treatment for Prostate Cancer: What to Expect
Surgery is a common treatment option for prostate cancer, particularly in cases where the cancer is localized and has not spread to other parts of the body. Prior to undergoing surgery, patients can expect a thorough evaluation of their overall health and prostate cancer stage to determine if surgery is the most appropriate course of action. Various surgical techniques may be used, including radical prostatectomy, which involves removing the entire prostate gland, and minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopic or robot-assisted surgery.
During the surgery, patients are typically placed under general anesthesia, ensuring they are asleep and free from pain. While each individual’s experience may vary, it is common to expect a hospital stay of several days following the procedure to monitor their recovery and manage any potential side effects. Post-surgery, patients can anticipate a temporary need for a urinary catheter to assist with urination, which will be removed once healing progresses. It is vital for patients to closely follow their surgeon’s instructions regarding post-operative care, physical activity restrictions, and medication regimens to optimize their recovery process.
Radiation Therapy: A Non-Invasive Approach to Prostate Cancer
Radiation therapy is a common treatment option for prostate cancer. It involves the use of high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells in the prostate gland. One of the key benefits of radiation therapy is that it is a non-invasive approach, meaning that it does not require any surgical incisions or invasive procedures.
During radiation therapy, a machine called a linear accelerator delivers precise beams of radiation to the prostate gland. The radiation damages the DNA of the cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing. Over time, the damaged cells die off, reducing the size of the tumor. Radiation therapy can be used as a primary treatment for localized prostate cancer or as an adjuvant treatment after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
A major advantage of radiation therapy is its ability to target cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Modern technology allows for highly targeted radiation beams, which can be customized to the specific shape and size of the tumor. This precision helps to spare nearby organs, such as the bladder and rectum, from unnecessary radiation exposure. Additionally, radiation therapy is typically administered in short sessions over several weeks, allowing patients to continue with their daily activities during treatment.
Hormone Therapy: Managing Prostate Cancer with Medication
Hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), is an essential treatment option for managing prostate cancer. It works by reducing the levels of male hormones, specifically testosterone, to slow down or stop the growth of prostate cancer cells. This therapy can be particularly beneficial in cases where the cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland or when other treatments have not been effective.
There are different approaches to hormone therapy, including medications that lower hormone levels or block their actions. The most commonly used medications are known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists and antagonists, which help to suppress the production of testosterone. These medications are typically administered as injections or implants and can be given on a regular schedule or as long-lasting formulations. Other hormone-blocking medications, such as anti-androgens, work by preventing testosterone from reaching the cancer cells. Hormone therapy may be used on its own or in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy, depending on the stage and characteristics of the cancer.
Chemotherapy for Prostate Cancer: Is it an Option for You?
Chemotherapy is a treatment option for prostate cancer that involves the use of powerful medications to target and destroy cancer cells in the body. It is generally recommended in cases where the cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland or has not responded to other forms of treatment. Chemotherapy drugs are usually given intravenously, but they can also be taken orally.
The decision to undergo chemotherapy is a complex one and should be made in consultation with your healthcare team. Factors such as the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, overall health, and individual preferences will be taken into consideration. It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy with your doctor to determine if it is the right option for you. While chemotherapy can be an effective treatment, it may also come with side effects that can impact your quality of life. It is important to have a thorough understanding of what to expect before making a decision.
• Chemotherapy is a treatment option for prostate cancer that targets and destroys cancer cells in the body.
• It is recommended when the cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland or hasn’t responded to other treatments.
• Chemotherapy drugs can be given intravenously or taken orally.
• The decision to undergo chemotherapy should be made in consultation with your healthcare team.
• Factors such as stage of cancer, aggressiveness, overall health, and personal preferences are considered.
• Discuss potential benefits and risks with your doctor before deciding on chemotherapy.
• Chemotherapy can be effective but may come with side effects that impact quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes for Prostate Cancer Patients: Diet and Exercise Tips
When it comes to managing prostate cancer, making certain lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. Diet plays a crucial role in supporting the body’s immune system and promoting optimal functioning. For prostate cancer patients, incorporating certain foods into their diet can help to combat inflammation, boost the immune system, and promote overall prostate health. Some foods that are recommended for prostate cancer patients include tomatoes, which are rich in lycopene—a powerful antioxidant; cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, which contain compounds that have been shown to help inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells; and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids that have anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, it is advised to limit the consumption of red and processed meats, as they have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
In addition to dietary adjustments, regular physical exercise is also an important aspect of managing prostate cancer. Exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving circulation, boosting immune function, and supporting overall well-being. Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for at least 150 minutes per week, along with strength-training exercises two or more days a week, is generally recommended for prostate cancer patients. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program, as they can provide personalized recommendations based on individual needs and capabilities. By incorporating a healthy diet and regular exercise into their lifestyle, prostate cancer patients can take proactive steps in managing their condition and promoting overall health and well-being.
| Lifestyle Changes for Prostate Cancer Patients | Key Concepts | Credible Source |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Diet | – Key Concept: Emphasize a plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for overall health. | American Cancer Society – Nutrition for Prostate Cancer |
| – Considerations: Plant-based diets may offer potential benefits in managing prostate cancer. | ||
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | – Key Concept: Include omega-3 fatty acids from sources like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts for anti-inflammatory effects. | Prostate Cancer Foundation – Diet and Lifestyle |
| – Considerations: Omega-3s may contribute to overall well-being and support prostate health. | ||
| Regular Exercise | – Key Concept: Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or aerobic exercises, to enhance overall health. | Cancer.net – Exercise and Prostate Cancer |
| – Considerations: Exercise can improve fatigue, mood, and treatment tolerance in prostate cancer patients. | ||
| Limiting Processed Foods | – Key Concept: Reduce processed foods, sugars, and red meats to promote a healthy and balanced diet. | Cancer.gov – Prostate Cancer Prevention |
| – Considerations: A nutrient-rich diet supports overall health and may impact cancer risk and progression. |
Managing Side Effects of Prostate Cancer Treatment
There are several side effects that individuals may experience as a result of prostate cancer treatment. One common side effect is erectile dysfunction, which refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection. This can greatly impact a man’s quality of life and sexual well-being. It is important for individuals to discuss this issue with their healthcare provider, as there are treatment options available to help manage this side effect. Medications such as Viagra or Cialis may be prescribed to improve erectile function, and there are also devices and techniques that can assist with achieving an erection.
Another common side effect of prostate cancer treatment is urinary incontinence, which is the involuntary leakage of urine. This can occur as a result of weakened pelvic floor muscles or damage to the nerves that control bladder function. Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen these muscles and improve urinary control. In some cases, medication or surgery may be necessary to address urinary incontinence. It is important for individuals to speak with their healthcare provider about their specific symptoms and concerns in order to receive appropriate management and support.
Emotional Well-being: Coping with the Psychological Impact of Prostate Cancer
Emotional well-being plays a crucial role in coping with the psychological impact of prostate cancer. A prostate cancer diagnosis can bring about a range of emotions, from fear and anxiety to sadness and uncertainty. It is important for patients to acknowledge and address these feelings in order to effectively manage their emotional well-being during this challenging time.
One of the key strategies for coping with the psychological impact of prostate cancer is to seek support. Connecting with others who have been through similar experiences can provide a sense of comfort and understanding. Support groups, both online and in-person, offer a safe space to share feelings, exchange advice, and find solace in the company of individuals who can relate to the challenges of prostate cancer. Additionally, talking to loved ones, family members, and friends about your emotions can provide a source of support and reassurance. Open and honest communication can bridge the gap between you and your loved ones, helping them understand your journey and allowing them to offer their support in meaningful ways.
Support Systems for Prostate Cancer Patients: Finding Help and Guidance
Support systems play a crucial role in providing assistance, guidance, and emotional support to prostate cancer patients. When faced with the challenges of this diagnosis, patients often find solace in connecting with others who have similar experiences. Support groups specifically tailored for prostate cancer patients can not only offer a safe space to share feelings but also provide valuable information and resources.
These support groups enable patients to discuss their concerns, fears, and questions with individuals who understand the physical and emotional impact of prostate cancer. Participating in support groups can be beneficial in several ways, such as reducing feelings of isolation, enhancing coping strategies, and fostering a sense of community. In addition to face-to-face support groups, online forums and communities have also become popular, allowing patients to connect with others from the comfort of their own homes. These virtual platforms provide convenience and accessibility, enabling individuals to seek guidance and support regardless of geographic location.
Life After Prostate Cancer: Strategies for Long-Term Recovery and Survivorship
After completing prostate cancer treatment, many men may find themselves wondering what comes next. Life after prostate cancer requires a shift in focus towards long-term recovery and survivorship. It’s important to understand that the road to recovery is different for every individual, and the strategies employed may vary depending on a person’s specific circumstances.
One of the key aspects of life after prostate cancer is maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Adopting a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall well-being. Additionally, regular exercise can play a crucial role in improving physical strength and reducing the risk of other health conditions. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can not only contribute to maintaining a healthy weight but also enhance cardiovascular health. Finding a balance between rest and activity is equally important, as it allows the body to recover and rebuild after treatment.
In addition to lifestyle changes, regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring your health and addressing any concerns or side effects that may arise. These appointments may include physical examinations, blood tests, imaging tests, and additional screenings as recommended by your doctor. Maintaining open and honest communication with your healthcare team is crucial during this time, as they can provide guidance on managing long-term side effects, monitoring for recurrence, and overall survivorship care. With proper care and attention, life after prostate cancer can be a time of renewal and continued well-being.
What are the types of prostate cancer?
There are two main types of prostate cancer: adenocarcinoma, which is the most common type, and rare types such as small cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors.
What are the risk factors for prostate cancer?
The risk factors for prostate cancer include age (being over 50), family history of prostate cancer, race (African Americans have a higher risk), and certain genetic mutations.
What are the common signs and symptoms of prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, some common signs include difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, and pain in the hips, back, or chest.
When should I seek medical help for prostate cancer?
It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any symptoms that could be related to prostate cancer or if you have risk factors. They can evaluate your condition and recommend appropriate tests or treatments.
What tests and procedures are used to diagnose prostate cancer?
Diagnostic tests for prostate cancer may include a digital rectal exam (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound, and a prostate biopsy.
What are the different treatment options for prostate cancer?
Treatment options for prostate cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. The choice of treatment depends on various factors such as cancer stage, grade, and individual patient preferences.
What can I expect during prostate cancer surgery?
Prostate cancer surgery, known as a prostatectomy, involves removing the prostate gland. It can be done through traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
Is radiation therapy a non-invasive approach to treating prostate cancer?
Yes, radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment option for prostate cancer. It uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells and can be delivered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy).
How does hormone therapy manage prostate cancer?
Hormone therapy aims to reduce the levels of male hormones (androgens) in the body, which can help slow down the growth of prostate cancer cells. It is often used in combination with other treatments.
Is chemotherapy an option for prostate cancer patients?
Chemotherapy is not commonly used as a first-line treatment for prostate cancer but may be considered in advanced cases or when other treatments have not been successful. It involves using drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
What lifestyle changes can help prostate cancer patients?
Prostate cancer patients can benefit from maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as regular exercise. These lifestyle changes can help manage side effects, improve overall well-being, and potentially reduce the risk of recurrence.
How can I manage the side effects of prostate cancer treatment?
Managing side effects of prostate cancer treatment may involve seeking medical advice, making lifestyle changes, taking prescribed medications, and utilizing supportive therapies such as physical therapy or counseling.
How can I cope with the psychological impact of prostate cancer?
Coping with the psychological impact of prostate cancer can be challenging. It is important to seek support from loved ones, join support groups, consider therapy or counseling, and engage in activities that promote emotional well-being.
Where can prostate cancer patients find help and guidance?
Prostate cancer patients can find help and guidance from various sources such as healthcare professionals, support groups, online communities, advocacy organizations, and educational resources specific to prostate cancer.
What strategies can help with long-term recovery and survivorship after prostate cancer?
Strategies for long-term recovery and survivorship after prostate cancer may include regular follow-up appointments, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, monitoring for signs of recurrence, seeking emotional support, and staying informed about advancements in prostate cancer care.






