The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Prostate Cancer Symptoms
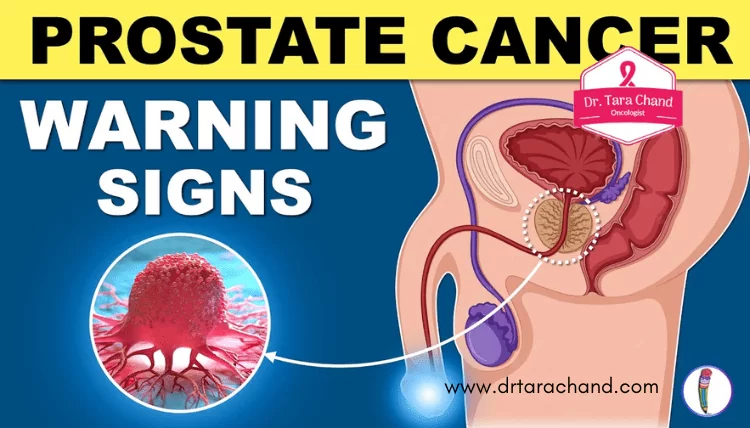
Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer

Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among men, and it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms associated with this condition. While early prostate cancer often does not cause any symptoms, as the disease progresses, men may experience a range of symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty in starting and stopping urination, weak urine flow, and blood in the urine or semen. Additionally, men with advanced prostate cancer may also experience bone pain, weight loss, and fatigue. However, it is crucial to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to prostate cancer and can also be caused by other conditions. Therefore, early detection through regular screenings is key in identifying and treating prostate cancer effectively.
In some cases, prostate cancer may cause more serious symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention. These include difficulty in urinating or the complete inability to pass urine, intense pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis, and the development of erectile dysfunction. If you experience any of these symptoms or have concerns about the health of your prostate, it is highly recommended to consult with a medical professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate medical guidance. Remember, timely detection and early intervention are crucial in improving outcomes and increasing the chances of successful treatment for prostate cancer.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a complex disease that affects millions of men worldwide. While the exact cause of prostate cancer is still unknown, there are certain risk factors that have been identified. Age is considered one of the most significant risk factors for prostate cancer, with the majority of cases occurring in men over the age of 50. In fact, the risk of developing prostate cancer increases significantly after the age of 65.
Another risk factor for prostate cancer is family history. Men who have a first-degree relative, such as a father or brother, who has been diagnosed with prostate cancer, are at a higher risk themselves. The risk becomes even greater if multiple family members have been affected. This suggests a genetic component to the development of prostate cancer, although specific genes associated with the disease have yet to be identified.
In addition to age and family history, race and ethnicity also play a role in prostate cancer risk. African American men have a higher incidence of prostate cancer compared to men of other racial and ethnic backgrounds. They are also more likely to be diagnosed at an advanced stage, which may contribute to poorer outcomes. On the other hand, Asian and Hispanic men tend to have a lower risk of prostate cancer. However, it is important to note that these differences in risk may be influenced by various factors, including genetic and environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and access to healthcare.
Modifiable risk factors, such as diet and lifestyle choices, have also been studied in relation to prostate cancer. While the evidence is not definitive, certain dietary factors, such as a high intake of red meat and dairy products, have been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly those containing lycopene, such as tomatoes, may help lower the risk. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight have also been suggested as potential protective factors against prostate cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand the impact of these lifestyle choices on prostate cancer risk.
It is important to remember that having one or more risk factors does not necessarily mean that an individual will develop prostate cancer. Conversely, some men without any known risk factors may still develop the disease. Understanding the risk factors associated with prostate cancer can help raise awareness and guide individuals towards proactive measures, such as regular screenings and lifestyle modifications, to reduce their risk. Further research is underway to uncover additional risk factors and refine our understanding of the complex interplay between genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices in relation to prostate cancer development.
Understanding the Prostate Gland
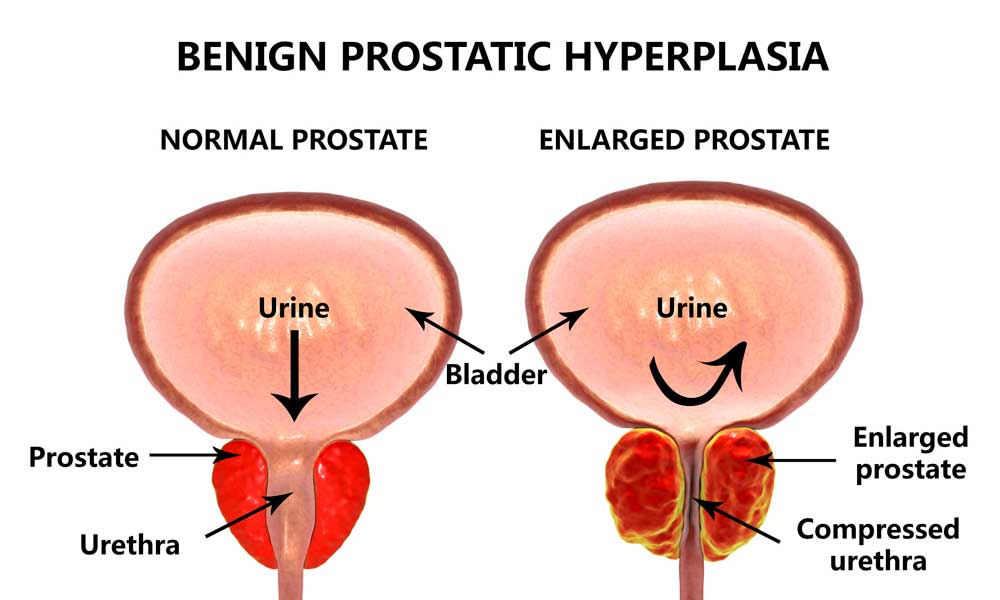
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. It plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system by producing the fluid that nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation. While the prostate gland is essential for reproduction, it also carries the risk of developing diseases, including prostate cancer.
The prostate gland undergoes changes as men age. It starts growing during puberty and continues to grow throughout adulthood. This process, known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can lead to urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty starting and stopping urination. Understanding the normal growth and function of the prostate gland is important for detecting and managing potential health issues in men.
Diagnostic Tests for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer among men worldwide. The importance of early detection cannot be emphasized enough, as it greatly impacts treatment success and overall prognosis. Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in detecting the presence of prostate cancer and determining its stage. There are several tests available for this purpose, including a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, digital rectal examination (DRE), and imaging tests such as a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The PSA blood test measures the levels of a protein produced by the prostate gland called prostate-specific antigen. Elevated PSA levels may indicate the presence of prostate cancer, but further investigation is needed to confirm the diagnosis. A DRE involves the doctor inserting a gloved finger into the rectum to feel the prostate for any abnormalities, such as lumps or hard areas. While this test can provide some initial information, it is not conclusive on its own and is often used in conjunction with other tests. Imaging tests, such as TRUS or MRI, provide detailed images of the prostate gland, allowing healthcare professionals to assess its size, shape, and any suspicious areas that may require further investigation.
Early detection through diagnostic tests is vital in the fight against prostate cancer. These tests serve as the first step in identifying potential abnormalities and determining the next course of action. It is important for men to understand the available diagnostic options and discuss them with their healthcare provider to make informed decisions about their prostate health. With timely detection and appropriate treatment, the outlook for individuals diagnosed with prostate cancer can be significantly improved.
Common Misconceptions about Prostate Cancer

Prostate cancer is a prevalent disease among men, and it is important to dispel some common misconceptions surrounding this condition. One misconception is that only older men are at risk for prostate cancer. While age is indeed a significant risk factor, it is crucial to note that prostate cancer can affect men of all ages. In fact, it is the most common cancer in men globally, with a wide range of ages affected. Therefore, it is essential for men, regardless of age, to be vigilant about their prostate health and undergo regular screenings as recommended by healthcare professionals.
Another misconception is that if a man has a family history of prostate cancer, he is destined to develop the disease. While having a family history does increase the risk, it does not guarantee the development of prostate cancer. It is true that men with a father or brother diagnosed with the disease have a higher risk, but it is important to recognize that genetics is just one factor among many. Other risk factors, such as age, ethnicity, and lifestyle choices, also play a significant role in the development of prostate cancer. Therefore, it is crucial for men with a family history to be aware of the increased risk and take proactive measures to monitor their prostate health through regular check-ups and appropriate screenings.
Misconceptions about prostate cancer can hinder awareness, prevention, and early detection efforts. It is crucial to debunk these myths, educate men about their risks, and encourage them to take appropriate measures to ensure their prostate health. By dispelling these misconceptions, we can empower men to make informed decisions about their well-being and work towards reducing the global burden of prostate cancer.
Early Detection of Prostate Cancer

Early detection of prostate cancer plays a crucial role in improving outcomes for patients. Regular screening and awareness of the warning signs can help detect the disease in its early stages when it is more treatable. One of the most common methods used for early detection is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. This test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate the presence of prostate cancer, although further diagnostic tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. It is important to note that PSA levels can be affected by various factors, such as age, inflammation, and enlargement of the prostate. Thus, it is essential to interpret the results in conjunction with other clinical findings to make an accurate assessment. Early detection also involves a digital rectal exam (DRE), where a healthcare professional manually examines the prostate gland for any abnormalities. Combining both the PSA test and DRE can provide a more comprehensive evaluation for early detection.
In addition to screening, it is crucial for individuals to be aware of the signs and symptoms of prostate cancer. These may include frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, and discomfort or pain in the pelvic area. While these symptoms may also be caused by other non-cancerous conditions, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if any of these signs persist or worsen. Early detection of prostate cancer can lead to timely intervention and an improved prognosis for patients. Therefore, it is vital for individuals, especially those at higher risk, such as older men or those with a family history, to prioritize regular screenings and remain vigilant about any potential symptoms they may experience.
Stages of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer can be classified into four stages, each representing a different extent of tumor growth and spread. In the early stage, known as stage I, the tumor remains confined within the prostate gland and is usually small in size. At this stage, the cancer is considered to be localized and may not cause any noticeable symptoms. Stage II prostate cancer involves a slightly larger tumor that is still confined within the prostate, but may be more aggressive or have a higher grade. It is important to note that at both stages I and II, the cancer has not spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
As prostate cancer progresses, it can advance to stage III, where the tumor extends beyond the prostate gland and may invade surrounding tissues and structures. At this stage, the cancer may spread to nearby seminal vesicles or the bladder. Typically, symptoms such as urinary problems, blood in the urine, or pain in the lower back or hips may become more evident. Stage IV prostate cancer is the most advanced stage, indicating that the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the bones, liver, or lungs. This is known as metastasis and can lead to a variety of symptoms depending on the affected organs.
Understanding the different stages of prostate cancer is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach and assessing the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with the disease. However, it is important to remember that each case is unique, and the stage alone does not solely dictate the course of treatment. Factors such as the individual’s overall health, age, and personal preferences also play a significant role in developing a comprehensive treatment plan. Thus, it is imperative to consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in prostate cancer management to receive personalized guidance and support.
• Stage I: The tumor remains confined within the prostate gland and is usually small in size.
• Stage II: A slightly larger tumor that is still confined within the prostate, but may be more aggressive or have a higher grade.
• Stage III: The tumor extends beyond the prostate gland and may invade surrounding tissues and structures. It may spread to nearby seminal vesicles or the bladder.
• Stage IV: The most advanced stage, indicating that the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as bones, liver, or lungs (metastasis).
• Symptoms become more evident as the cancer progresses, including urinary problems, blood in urine, or pain in lower back or hips.
Understanding these stages helps determine appropriate treatment approaches and assess prognosis for individuals with prostate cancer. However, each case is unique and other factors like overall health and personal preferences also play a role in developing a treatment plan. Consulting healthcare professionals specializing in prostate cancer management provides personalized guidance and support.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease, and the choice of treatment options depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, the overall health of the patient, and their personal preferences. Some of the common treatment options for prostate cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy.
Surgery, such as a radical prostatectomy, involves the complete removal of the prostate gland. This procedure may be recommended for patients with localized prostate cancer. Radiation therapy, on the other hand, uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It can be performed externally (external beam radiation therapy) or internally (brachytherapy). Hormone therapy aims to block or reduce the levels of male hormones (e.g., testosterone), as these hormones can promote the growth of prostate cancer cells. Chemotherapy, meanwhile, involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells and may be recommended for advanced or metastatic prostate cancer.
Each treatment option has its own benefits and potential side effects, so it is crucial for patients to discuss these options with their healthcare team and make an informed decision. The choice of treatment should take into account the individual’s overall health, the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, as well as their personal preferences. Additionally, ongoing research and advancements in the field continue to provide hope for more targeted and effective treatments for prostate cancer.
Side Effects of Prostate Cancer Treatments
Prostate cancer treatments, such as surgery, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy, can be effective in managing the disease. However, they may also come with a variety of side effects that can impact a man’s quality of life. One common side effect of these treatments is erectile dysfunction, which can make it difficult for a man to achieve or maintain an erection. This can be distressing for both the patient and their partner, and can have a significant impact on their sexual well-being. It is important for men to discuss this potential side effect with their healthcare provider before starting treatment, as there are options available to help manage this issue. In addition to erectile dysfunction, other side effects of prostate cancer treatments can include urinary incontinence, fatigue, hot flashes, and changes in bowel habits. While these side effects can be challenging to deal with, it is crucial for patients to communicate openly with their healthcare team about their symptoms, as there may be strategies or interventions that can help alleviate them.
Managing Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Prostate cancer symptoms can vary from person to person and may range from mild to severe. It is important for individuals with prostate cancer to work closely with their healthcare team to manage and alleviate these symptoms effectively.
One common symptom of prostate cancer is urinary problems. As the prostate gland enlarges or tumors develop, it can put pressure on the urethra, leading to difficulties in urination. This may include frequent urination, weak urine flow, pain or burning during urination, or the inability to completely empty the bladder. Management strategies may involve lifestyle modifications such as avoiding caffeine and alcohol, practicing pelvic floor exercises, and drinking plenty of water. Additionally, medications or surgical interventions may be recommended to help address these urinary symptoms.
Another symptom that individuals with prostate cancer may experience is sexual dysfunction. The cancer itself, as well as its treatments, can impact sexual function. This may manifest as erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, or difficulty achieving orgasm. Healthcare providers may explore various options to help manage these symptoms, including counseling, medication, or aids such as vacuum erection devices. Open communication with healthcare professionals is key to receiving appropriate guidance and support in addressing these challenges.
Managing prostate cancer symptoms requires an individualized approach that takes into account the specific circumstances and needs of each patient. By working closely with healthcare providers, patients can explore various strategies and interventions to help improve their quality of life while managing the symptoms associated with prostate cancer.
Certainly! Here’s a short data table on understanding prostate cancer symptoms:
| Understanding Prostate Cancer Symptoms | Key Concepts | Credible Source |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary Changes | – Key Concept: Changes in urinary habits, such as frequency, urgency, or difficulty urinating, may signal prostate issues. | American Cancer Society – Prostate Cancer Symptoms |
| – Considerations: Monitoring and reporting any urinary changes to a healthcare professional is crucial. | ||
| Erectile Dysfunction | – Key Concept: Prostate cancer can impact sexual function, leading to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. | Prostate Cancer Foundation – Prostate Cancer and Sexual Function |
| – Considerations: Addressing changes in sexual function is part of comprehensive prostate health care. | ||
| Pelvic Pain or Discomfort | – Key Concept: Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, hips, or lower back may be associated with advanced prostate cancer. | Mayo Clinic – Prostate Cancer Symptoms |
| – Considerations: Identifying and evaluating persistent discomfort is essential for early detection. | ||
| Blood in Urine or Semen | – Key Concept: The presence of blood in urine or semen may indicate prostate issues, including cancer. | Cancer.gov – Prostate Cancer Symptoms |
| – Considerations: Any unexplained bleeding should prompt further medical investigation. |
Supportive Care for Prostate Cancer Patients
Supportive care plays a crucial role in the management of prostate cancer patients, as it aims to improve the overall quality of life and alleviate the physical and emotional symptoms associated with the disease and its treatment. One important aspect of supportive care is pain management. Prostate cancer can cause pain in various areas, including the lower back, hips, and pelvic region. Effective pain control strategies, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioid medications, can help relieve pain and improve daily functioning.
In addition to pain management, supportive care for prostate cancer patients also focuses on addressing the side effects of treatment. For instance, many individuals undergoing hormonal therapy may experience hot flashes, fatigue, and sexual dysfunction. In such cases, healthcare providers can prescribe medications or recommend lifestyle modifications to manage these symptoms. Moreover, emotional support is essential for patients and their families. Support groups, counseling services, and educational resources can provide psychological support and help individuals navigate the challenges associated with prostate cancer. By embracing a comprehensive approach to supportive care, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the well-being of prostate cancer patients.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Prostate Cancer Risk
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men, but there are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk. Making healthy choices in terms of diet and exercise is crucial in lowering the chances of developing prostate cancer. Research has shown that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while low in red meat and saturated fats, can play a significant role in preventing prostate cancer. Additionally, regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, has been linked to a lower risk of prostate cancer. It is important to note that while these lifestyle changes can reduce the risk, they do not guarantee complete prevention. Consulting with a healthcare professional is always recommended for personalized advice regarding diet and exercise modifications.
In addition to dietary and exercise modifications, maintaining a healthy weight is essential in reducing the risk of prostate cancer. Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, weight management becomes more attainable. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are also crucial lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk. Alcohol has been shown to increase the risk of developing prostate cancer, especially when consumed in large amounts. Furthermore, quitting smoking not only reduces the risk of prostate cancer but also lowers the chances of developing other types of cancer and various health complications. Implementing these lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on overall health and well-being while effectively reducing the risk of prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Research and Advances
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in prostate cancer research that have revolutionized the way we understand and treat this disease. One major area of focus has been on improving diagnostic techniques. Traditional methods, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, have limitations in terms of accuracy and identifying aggressive forms of prostate cancer. However, researchers have developed new blood tests, such as the prostate health index (PHI) and the 4Kscore test, that provide more precise information about the risk of prostate cancer. These tests take into account multiple biomarkers and have shown promising results in identifying clinically significant prostate cancer, potentially reducing unnecessary biopsies and overdiagnosis.
Another exciting avenue of research in the field of prostate cancer is the exploration of targeted therapies. Traditional treatment approaches, such as surgery and radiation therapy, can often have significant side effects and impact the patient’s quality of life. However, researchers have identified specific molecular targets within prostate cancer cells that can be exploited for more effective and less toxic treatments. For example, drugs like enzalutamide and abiraterone acetate have been developed to target androgen receptors, which play a crucial role in the growth of prostate cancer cells. These targeted therapies have shown remarkable efficacy in improving overall survival and delaying disease progression in advanced prostate cancer patients.
There is no doubt that the advancements in prostate cancer research have opened up new possibilities for early detection and more targeted treatments. However, it is important to remember that each individual’s case is unique, and treatment decisions should always be based on a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. With the continuous progress in research and the collaborative efforts of scientists, physicians, and patients, we can hope for further breakthroughs in understanding, preventing, and treating prostate cancer in the future.
Prostate Cancer Prevention Strategies
It is important for men to be proactive in reducing their risk of developing prostate cancer. While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, certain strategies can help lower the risk and promote overall prostate health. One key approach is maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle. Research suggests that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while reducing the consumption of red and processed meats, can lower the risk of developing prostate cancer. Additionally, regular exercise has been linked to a decreased risk of prostate cancer. Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity most days of the week can have a positive impact on prostate health.
Besides a healthy diet and lifestyle, understanding and managing risk factors can also play a crucial role in prostate cancer prevention. Age, family history, and race are among the factors that cannot be controlled. However, there are factors that can be modified, such as environmental exposures and occupational hazards. Minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins, practicing safe occupational practices, and seeking protective measures when necessary can help reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer. It is important for individuals to be aware of the potential risks associated with their environment and take necessary precautions to protect their prostate health.
What are the signs and symptoms of prostate cancer?
Common signs and symptoms of prostate cancer include difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, and bone pain.
What are the risk factors for prostate cancer?
Risk factors for prostate cancer include age (being over 50), family history of prostate cancer, certain genetic factors, race (African Americans have a higher risk), and obesity.
What is the prostate gland and its role?
The prostate gland is a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
What are the diagnostic tests for prostate cancer?
Diagnostic tests for prostate cancer may include a digital rectal exam (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, imaging tests (such as ultrasound or MRI), and a prostate biopsy.
What are some common misconceptions about prostate cancer?
Some common misconceptions about prostate cancer include the belief that only older men can get it, that it always causes noticeable symptoms, and that a high PSA level automatically means cancer.
How is prostate cancer detected early?
Prostate cancer can be detected early through regular screening, including PSA blood tests and DREs, especially for men at higher risk.
What are the stages of prostate cancer?
The stages of prostate cancer range from Stage I (localized within the prostate) to Stage IV (advanced and spread to other parts of the body).
What are the treatment options for prostate cancer?
Treatment options for prostate cancer include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
What are the side effects of prostate cancer treatments?
Side effects of prostate cancer treatments may include urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, bowel problems, and hormonal changes.
How can prostate cancer symptoms be managed?
Prostate cancer symptoms can be managed through various approaches, including medications, lifestyle changes, pain management techniques, and psychological support.
What supportive care is available for prostate cancer patients?
Supportive care for prostate cancer patients may include counseling, support groups, palliative care, and specialized services to address the physical, emotional, and practical needs of patients.
What lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of prostate cancer?
Lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of prostate cancer include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
What are the latest research and advances in prostate cancer?
Ongoing research and advances in prostate cancer focus on developing new treatments, improving early detection methods, understanding genetic factors, and exploring targeted therapies.
What are some strategies for preventing prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer prevention strategies include regular screenings, adopting a healthy lifestyle, understanding and managing risk factors, and staying informed about new research and advances in the field.






