The Latest Breakthroughs in Prostate Cancer Screening: What You Need to Know
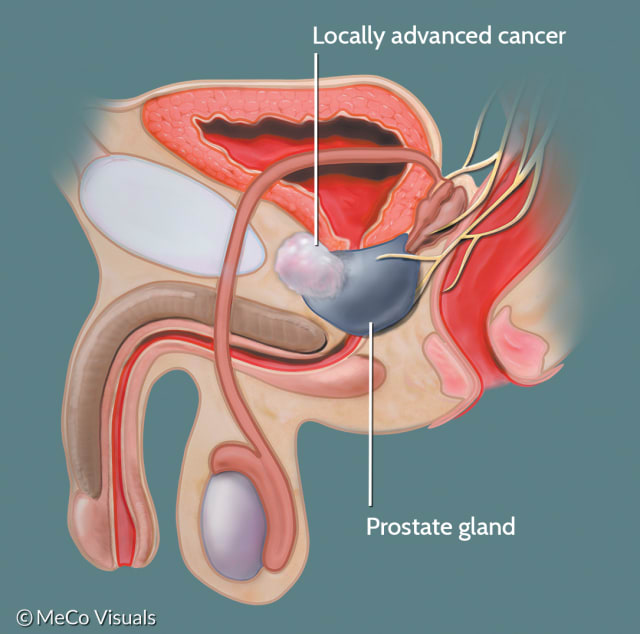
Understanding Prostate Cancer: Causes and Risk Factors
Prostate cancer is a complex disease that arises from multiple factors, including genetic predisposition and environmental influences. While the exact causes of prostate cancer are not fully understood, certain risk factors have been identified. Age is the most significant risk factor, with the incidence of prostate cancer increasing with advancing age. In fact, it is estimated that over 80% of prostate cancer cases occur in men aged 65 and older. Other risk factors include family history, race, and certain lifestyle factors such as smoking and a diet high in saturated fats.
Genetics also play a crucial role in prostate cancer development. Studies have shown that men with a family history of prostate cancer have an increased risk of developing the disease themselves. Mutations in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, have also been associated with an elevated risk of prostate cancer. Additionally, certain genetic variants can affect how the body processes hormones that can influence prostate cancer development. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with prostate cancer is essential for early detection and prevention strategies.
The Importance of Early Detection in Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide, and early detection plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes. Detecting prostate cancer at an early stage allows for more effective management and potentially better long-term prognosis. One of the main reasons why early detection is important is because prostate cancer often starts with no symptoms or with mild symptoms that may be easily overlooked. By the time symptoms become noticeable, the cancer may have already advanced to a more aggressive stage, making it harder to treat.
Early detection of prostate cancer can be achieved through regular screening tests, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test and digital rectal examination (DRE). The PSA test measures the levels of a protein called prostate-specific antigen in the blood, which can be elevated in men with prostate cancer. The DRE involves a physical examination of the prostate gland by a healthcare professional to check for any abnormalities or changes in its size or texture. These screening tests, although not perfect, can help identify potential cases of prostate cancer, allowing for prompt referral to a specialist for further investigation and appropriate treatment if necessary.
While early detection is crucial, it is important to note that screening for prostate cancer also has its limitations and potential risks. False-positive results, where the screening test indicates the presence of cancer when none is actually present, can lead to unnecessary anxiety and further invasive testing. Additionally, prostate cancer is a complex disease with varying aggressiveness and treatment options, and not all cases will benefit from early intervention. Therefore, it is essential for men to discuss the benefits and risks of prostate cancer screening with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision based on their individual circumstances.
• Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide
• Early detection improves treatment outcomes and long-term prognosis
• Prostate cancer often starts with no symptoms or mild symptoms that may be overlooked
• By the time symptoms become noticeable, the cancer may have already advanced to a more aggressive stage
• Regular screening tests like PSA blood test and DRE can achieve early detection of prostate cancer
• PSA test measures levels of prostate-specific antigen in the blood, which can be elevated in men with prostate cancer
• DRE involves physical examination of the prostate gland to check for abnormalities or changes in size or texture
• Screening tests help identify potential cases of prostate cancer for further investigation and treatment if necessary
• Screening for prostate cancer has limitations and potential risks
– False-positive results can lead to unnecessary anxiety and invasive testing
– Not all cases will benefit from early intervention due to varying aggressiveness and treatment options
• Men should discuss benefits and risks with healthcare provider before deciding on screening
Common Symptoms of Prostate Cancer to Watch Out For
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men, and being aware of its symptoms is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. While the symptoms of prostate cancer may vary between individuals, there are several common signs that men should watch out for.
One of the primary symptoms of prostate cancer is the presence of urinary changes. Men may experience a frequent need to urinate, especially during the night. They may also observe a weak or interrupted urine flow, or have difficulty starting and stopping urination. Additionally, some men may notice blood in their urine or semen, which can be a cause for concern. These urinary symptoms should not be ignored, as they may indicate an underlying issue, such as prostate cancer.
Traditional Methods of Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer screening has been a crucial aspect of early detection and prevention strategies for many years. Traditional methods of screening primarily involve the use of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test and digital rectal examination (DRE). These methods aim to identify any abnormal changes in the prostate gland that may be indicative of cancer.
The PSA blood test measures the levels of a protein called prostate-specific antigen in the blood, which is produced by the prostate gland. While elevated levels of PSA may suggest the presence of prostate cancer, it is important to note that PSA levels can also be elevated due to non-cancerous conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate inflammation. This can sometimes lead to false-positive results, prompting further investigations and potential unnecessary anxiety for the individual. Additionally, the PSA test has limitations in its ability to distinguish aggressive cancers from indolent ones, which can lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment. The DRE, on the other hand, involves a physical examination of the prostate gland through the rectum. It can provide valuable information regarding the size, texture, and abnormalities of the gland. However, this method may also have limitations in its sensitivity and specificity, making it less reliable as a standalone screening tool.
While traditional methods of prostate cancer screening have played a significant role in the early detection of the disease, they have their limitations. As medical advancements continue, researchers are exploring new technologies and approaches to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of screening methods. The development of more precise and reliable screening techniques could help reduce unnecessary procedures and improve the overall outcomes for individuals at risk of prostate cancer. The challenges and opportunities in improving prostate cancer screening will be discussed further in this article.
Limitations of Traditional Prostate Cancer Screening
Traditional methods of prostate cancer screening, such as digital rectal exam (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, have been instrumental in detecting the disease at an early stage. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of these conventional screening approaches.
One limitation is the lack of specificity in the PSA test. Elevated PSA levels can be indicative of various conditions other than prostate cancer, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or inflammation. This can lead to false-positive results, causing unnecessary anxiety and further invasive procedures like biopsies. Additionally, PSA levels can fluctuate for reasons unrelated to cancer, making it challenging to determine the exact cause of elevated levels.
Another limitation lies in the sensitivity of traditional screening methods. The PSA test can miss some cases of prostate cancer, especially in its early stages. This can result in false-negative results, providing individuals with a falsely reassuring sense of their prostate health. As a result, there is a need for more comprehensive screening approaches that can effectively detect prostate cancer, especially in its early and potentially curable stage.
As research continues to evolve, efforts are being made to address these limitations and improve the accuracy and reliability of prostate cancer screening. By exploring advancements in technology, genetic testing, and non-invasive approaches, we can hope for more effective methods that enhance early detection and improve prostate cancer outcomes.
| Limitations of Traditional Prostate Cancer Screening | Key Concepts | Credible Source |
|---|---|---|
| PSA Test Specificity | – Key Concept: PSA tests may yield false positives, leading to unnecessary anxiety and interventions. | American Cancer Society – Limitations of PSA Testing |
| – Considerations: Elevated PSA levels can occur without cancer, affecting test reliability. | ||
| Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment | – Key Concept: Screening may detect slow-growing cancers that may not require treatment. | National Cancer Institute – Prostate Cancer Screening |
| – Considerations: Overtreatment can result in unnecessary side effects and quality of life impacts. | ||
| Risk of Biopsy Complications | – Key Concept: Biopsies, often prompted by abnormal screenings, carry risks of infection and bleeding. | Mayo Clinic – Prostate Biopsy |
| – Considerations: Complications emphasize the need for cautious use of biopsies. | ||
| Limited Sensitivity for Aggressive Cancers | – Key Concept: Some screening methods may not effectively identify aggressive forms of prostate cancer. | Urology Care Foundation – Prostate Cancer |
| – Considerations: Aggressive cancers may be missed with traditional screening approaches. |
Advancements in Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Testing
PSA testing has been a widely used method for prostate cancer screening. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in this area to improve the accuracy and reliability of PSA testing. One of the notable advancements is the introduction of the PSA velocity and PSA doubling time measurements. These measurements provide additional information about the progression and aggressiveness of prostate cancer, allowing for better risk stratification and treatment decisions.
Another important advancement in PSA testing is the development of different PSA isoforms and molecular forms. This has led to the introduction of tests such as the free PSA and complexed PSA, which can provide a more comprehensive evaluation of prostate health. By measuring different forms of PSA, clinicians can get a better understanding of the likelihood of prostate cancer presence and distinguish it from other benign conditions.
The advancements in PSA testing have certainly improved the accuracy and sensitivity of prostate cancer screening. However, it’s vital to remember that PSA testing alone cannot provide a definitive diagnosis for prostate cancer. False-positive results can occur, leading to unnecessary biopsies and anxiety for patients. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the limitations of PSA testing and combine it with other screening methods to improve the overall accuracy and reliability of prostate cancer detection.
The Role of Genetic Testing in Prostate Cancer Screening
Genetic testing has emerged as a valuable tool in the screening and detection of prostate cancer. By analyzing an individual’s genes, scientists and healthcare professionals can better understand the risk factors and potential likelihood of developing the disease. This type of test examines specific genes that are known to be associated with prostate cancer, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2. By identifying any mutations or abnormalities in these genes, doctors can determine if a person has an increased risk of developing prostate cancer.
Furthermore, genetic testing can also provide valuable information for treatment decisions. Certain genetic mutations may indicate a heightened sensitivity or resistance to specific types of treatments, such as hormone therapy or chemotherapy. This knowledge can help doctors tailor the treatment plan to each patient’s individual genetic profile, potentially leading to more effective outcomes. It is important to note that genetic testing for prostate cancer is not recommended for everyone. Instead, it is typically reserved for individuals with a strong family history of the disease or those who have already been diagnosed. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if genetic testing is appropriate for you or your loved ones.
Emerging Technologies for Prostate Cancer Detection

Emerging technologies have brought about significant advancements in the field of prostate cancer detection. These innovative approaches aim to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of screening methods, ultimately leading to early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
One such technology is the liquid biopsy, which holds promise in the detection of prostate cancer. Liquid biopsy involves the analysis of blood or other bodily fluids to identify cancer biomarkers. This non-invasive approach provides a convenient and accessible method for screening high-risk individuals and monitoring disease progression. Research has shown that liquid biopsy can detect genetic mutations and other molecular changes associated with prostate cancer, helping doctors make more informed treatment decisions.
Additionally, MRI imaging has emerged as a valuable tool in enhancing the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Magnetic resonance imaging allows for detailed visualization of the prostate gland, helping to identify suspicious areas and guide biopsy procedures. By providing a more accurate assessment of tumor size, location, and aggressiveness, MRI imaging can aid in personalized treatment planning and reduce unnecessary invasive procedures.
Overall, the development of emerging technologies for prostate cancer detection holds great promise in improving screening accuracy and patient outcomes. Continued research and advancements in these areas are essential in the fight against this prevalent disease. However, further validation and clinical trials are needed to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of these technologies before widespread implementation can occur.
Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Tool for Prostate Cancer Screening
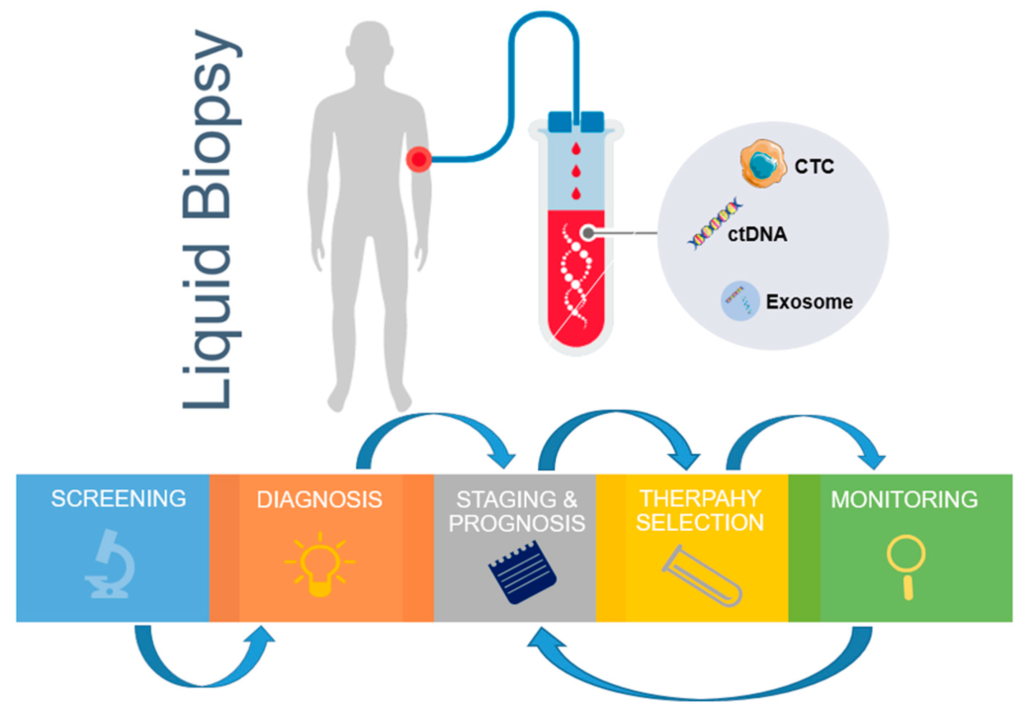
Liquid biopsy, a non-invasive method for detecting and monitoring cancer, has emerged as a promising tool in the screening and diagnosis of prostate cancer. Unlike traditional methods that require invasive procedures such as biopsies, liquid biopsy offers a less invasive and more convenient alternative.
This innovative technique involves the analysis of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in the blood. By detecting genetic alterations, such as mutations or rearrangements, liquid biopsy can provide valuable information about the presence and progression of prostate cancer. Not only can this method help identify individuals at high risk of developing the disease, but it also holds great potential for monitoring treatment response and detecting the emergence of resistance mutations. The ability to obtain real-time information through a simple blood draw makes liquid biopsy an attractive option in the field of prostate cancer screening. However, further research is needed to validate its clinical utility and establish standardized protocols for its implementation.
In conclusion, liquid biopsy shows promise as a powerful tool in the screening and monitoring of prostate cancer. With its non-invasive nature and potential for real-time monitoring, this technique could revolutionize the way we detect and manage this prevalent cancer. While there are still challenges to overcome and more research to be done, the potential benefits of liquid biopsy make it an area of great interest and excitement in the field of prostate cancer screening. By continuing to explore and refine this innovative approach, we may be able to improve early detection rates, enhance treatment outcomes, and ultimately save more lives affected by prostate cancer.
MRI Imaging: Enhancing Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
MRI imaging has proven to be a valuable tool in enhancing the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Unlike traditional methods such as digital rectal examination (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, MRI provides a non-invasive and detailed visualization of the prostate gland. By utilizing powerful magnets and radio waves, MRI can generate high-resolution images, allowing physicians to detect abnormalities and evaluate the extent of cancerous growth within the prostate.
One of the major advantages of MRI imaging in prostate cancer diagnosis is its ability to distinguish between benign and malignant tumors. With its superior soft tissue contrast, MRI can differentiate between healthy prostate tissue and cancerous lesions, aiding in accurate diagnosis. Additionally, MRI can provide valuable information about the size, location, and multiplicity of tumors, which is crucial for treatment planning and monitoring disease progression. The sensitivity and specificity of MRI in detecting prostate cancer have been shown to be superior to traditional screening methods, making it a valuable addition to the diagnostic armamentarium.
The Potential of Artificial Intelligence in Prostate Cancer Screening
Artificial intelligence (AI) has shown great potential in prostate cancer screening, revolutionizing the way this disease is detected and diagnosed. With its ability to analyze large amounts of medical data, AI algorithms have the power to detect patterns and identify potential abnormalities that may be indicative of prostate cancer. By utilizing machine learning techniques, AI can learn from past cases and continuously improve its accuracy in identifying cancerous cells or tumors within the prostate gland.
One of the key advantages of AI in prostate cancer screening is its ability to analyze medical images, such as MRI scans, with exceptional precision. AI algorithms can identify subtle changes in prostate tissue morphology and texture that might go unnoticed by human observers. This level of accuracy can help reduce false negatives and false positives, ensuring that patients receive appropriate follow-up care and treatment. Additionally, AI can also aid in the integration of various imaging modalities, enhancing the diagnostic process further.
Non-Invasive Approaches for Prostate Cancer Detection
Non-invasive approaches for prostate cancer detection have become an area of intense research and development in recent years. These techniques aim to provide a more accurate and convenient method of detecting prostate cancer without the need for invasive procedures, such as biopsies or surgeries. One such approach involves the use of biomarkers, which are specific substances or molecules that can indicate the presence of cancer in the body. By analyzing these biomarkers in urine or blood samples, researchers can identify potential signs of prostate cancer and provide early detection.
Another promising non-invasive approach is the use of imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to visualize the prostate and identify any abnormalities or tumors. MRI imaging has shown great potential in enhancing the diagnosis of prostate cancer, as it can provide detailed images of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues, allowing doctors to accurately detect and stage the cancer. Furthermore, advancements in MRI technology, such as multiparametric MRI, have improved the sensitivity and specificity of detection, leading to more precise diagnosis and treatment planning for patients with prostate cancer.
Non-invasive approaches for prostate cancer detection are revolutionizing the field of screening and diagnosis. These techniques offer the potential for early detection, improved accuracy, and reduced patient discomfort. As further research and development continue, it is likely that non-invasive approaches will play a crucial role in enhancing prostate cancer screening and ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The Future of Prostate Cancer Screening: Personalized Medicine
As advancements continue to unfold in the field of medicine, personalized medicine is emerging as a promising approach for prostate cancer screening. Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, takes into account an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and other relevant data to tailor medical interventions specifically to their needs. By focusing on the individual characteristics of each patient, personalized medicine has the potential to enhance the accuracy of prostate cancer screening and improve patient outcomes.
One of the key advantages of personalized medicine in prostate cancer screening is the ability to identify individuals who are at a higher risk of developing the disease. By analyzing an individual’s genetic profile, doctors can identify specific gene mutations or variants that predispose them to prostate cancer. This knowledge allows for more targeted screening strategies and surveillance plans, ensuring that high-risk individuals receive the necessary attention and interventions at an earlier stage. Additionally, personalized medicine enables the identification of individuals who are at a lower risk of developing prostate cancer, sparing them from unnecessary invasive tests and interventions.
Improving Prostate Cancer Screening: Challenges and Opportunities
Prostate cancer remains a significant healthcare challenge, and improving screening methods is crucial for early detection and better treatment outcomes. One of the key challenges faced in prostate cancer screening is the limitations of traditional methods, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. While PSA testing has been widely used, it has been associated with high false-positive rates and cannot accurately differentiate between aggressive and indolent prostate cancers. This poses a challenge in identifying those who truly require further diagnostic procedures and treatment.
However, opportunities for improving prostate cancer screening have emerged through advancements in technology. Liquid biopsy, for instance, shows promise as a non-invasive tool for early detection and monitoring of prostate cancer. By analyzing circulating tumor DNA and other biomarkers, liquid biopsies can provide valuable information about the presence and progression of prostate cancer, allowing for more personalized treatment approaches. Additionally, MRI imaging has been increasingly utilized to enhance prostate cancer diagnosis. With its superior visualization of the prostate gland, MRI imaging can help detect and characterize tumors more accurately, aiding in treatment planning and decision-making.
In conclusion, while challenges persist, advancements in prostate cancer screening offer valuable opportunities for improved outcomes. Embracing emerging technologies, such as liquid biopsy and MRI imaging, can enhance early detection, treatment planning, and overall management of prostate cancer. By further exploring innovative approaches and overcoming existing limitations, we can pave the way for a future where personalized medicine plays a pivotal role in prostate cancer screening and ultimately improves patient outcomes.
What are the common symptoms of prostate cancer?
Common symptoms of prostate cancer include frequent urination, difficulty starting and stopping urination, weak urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, and erectile dysfunction.
What are the traditional methods of prostate cancer screening?
Traditional methods of prostate cancer screening include digital rectal exam (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test.
What are the limitations of traditional prostate cancer screening?
The limitations of traditional prostate cancer screening include a high rate of false positives, leading to unnecessary biopsies, and the inability to distinguish between aggressive and slow-growing tumors.
What advancements have been made in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing?
Advancements in PSA testing include the use of different PSA cutoffs based on age, PSA velocity, and PSA density to improve accuracy in detecting prostate cancer.
What is the role of genetic testing in prostate cancer screening?
Genetic testing can help identify individuals who are at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, allowing for more targeted screening and early detection.
What are emerging technologies for prostate cancer detection?
Emerging technologies for prostate cancer detection include liquid biopsy and MRI imaging, which offer non-invasive alternatives to traditional screening methods.
How does liquid biopsy contribute to prostate cancer screening?
Liquid biopsy involves testing a blood sample for circulating tumor cells or genetic material released by cancer cells, providing a less invasive and potentially more accurate method for detecting prostate cancer.
How does MRI imaging enhance prostate cancer diagnosis?
MRI imaging allows for detailed visualization of the prostate gland, helping to identify suspicious areas and guide targeted biopsies, leading to more accurate diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer.
What is the potential of artificial intelligence in prostate cancer screening?
Artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns and markers indicative of prostate cancer, potentially improving the accuracy and efficiency of screening.
What non-invasive approaches are being explored for prostate cancer detection?
Non-invasive approaches being explored for prostate cancer detection include urine-based tests, biomarker analysis, and imaging techniques that do not require invasive procedures.
How does personalized medicine contribute to the future of prostate cancer screening?
Personalized medicine aims to tailor screening and treatment strategies based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and risk profile, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of prostate cancer screening.
What are the challenges and opportunities in improving prostate cancer screening?
The challenges and opportunities in improving prostate cancer screening include reducing false positives and overdiagnosis, identifying high-risk individuals more accurately, integrating new technologies into clinical practice, and promoting awareness and accessibility of screening programs.






