Anxiety vs. Stress: What’s the Difference and How to Manage Both

Understanding the Nature of Anxiety and Stress

Anxiety and stress are two common and closely related emotional experiences that can have a significant impact on our overall well-being. Understanding the nature of anxiety and stress is crucial in order to effectively manage and reduce their presence in our lives.
Anxiety can be described as a feeling of apprehension or fear about a future event. It is a natural response to situations perceived as threatening or challenging. While it is normal to feel anxious from time to time, excessive and persistent anxiety can be debilitating and interfere with daily life activities. On the other hand, stress is a response to external pressures or demands, often triggered by difficult or overwhelming circumstances. It can manifest in physical, emotional, and cognitive symptoms, such as muscle tension, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Both anxiety and stress can have detrimental effects on our mental and physical health if left unaddressed. According to the World Health Organization, anxiety disorders are the most common mental disorders globally, with around 275 million people affected. These conditions can contribute to the development of other health issues, such as depression, substance abuse, and chronic pain. The impact of anxiety and stress extends beyond mental health, as it can also lead to increased risks of cardiovascular disease, weakened immune system, and gastrointestinal problems. It is therefore crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of anxiety and stress in order to effectively address and manage these conditions.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety and Stress
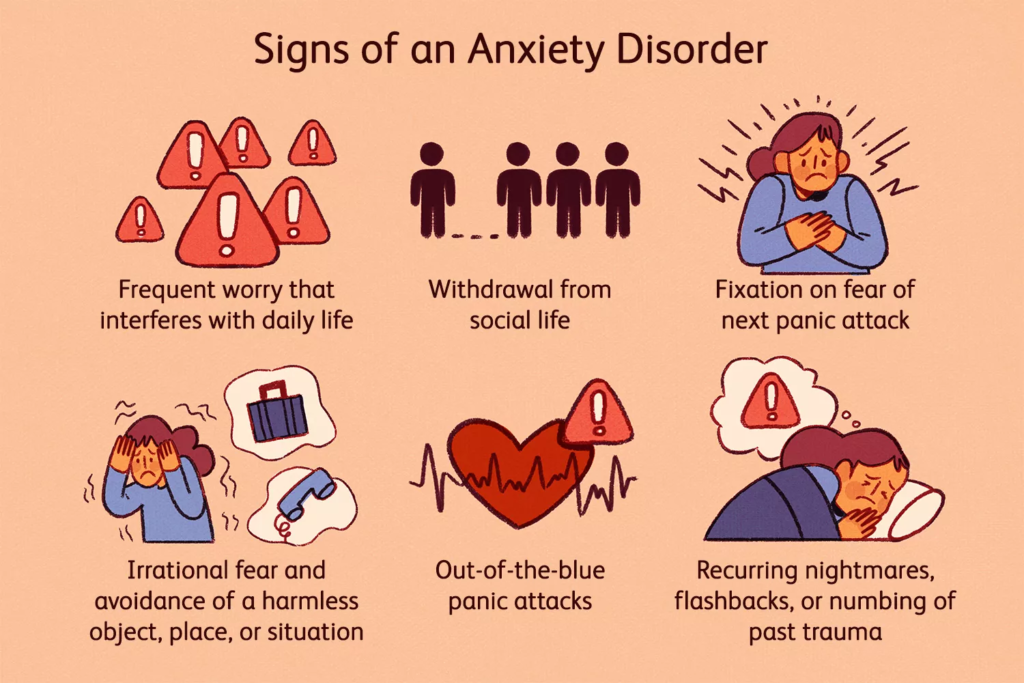
Anxiety and stress can manifest in various ways, impacting both our mental and physical well-being. It is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of these conditions to seek appropriate help and support. Some common signs of anxiety include persistent feelings of worry or fear, racing thoughts, irritability, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, and a sense of impending doom. The physical symptoms can include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, muscle tension, headaches, stomachaches, and sleep disturbances.
Stress, on the other hand, often presents itself differently. It can lead to feelings of overwhelm, a sense of being unable to cope with demands, excessive worrying, and persistent feelings of tension or pressure. Physically, stress might manifest as fatigue, frequent headaches, muscle tension, changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, and digestive problems. It is important to note that anxiety and stress can coexist, and their symptoms might overlap, making it essential to seek professional guidance to differentiate between the two.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of anxiety and stress empowers us to take proactive steps towards managing these conditions effectively. By recognizing these indicators, individuals can seek appropriate support, implement healthy coping mechanisms, and make necessary lifestyle changes to alleviate the impact of anxiety and stress on their overall well-being.
Differentiating Between Anxiety and Stress
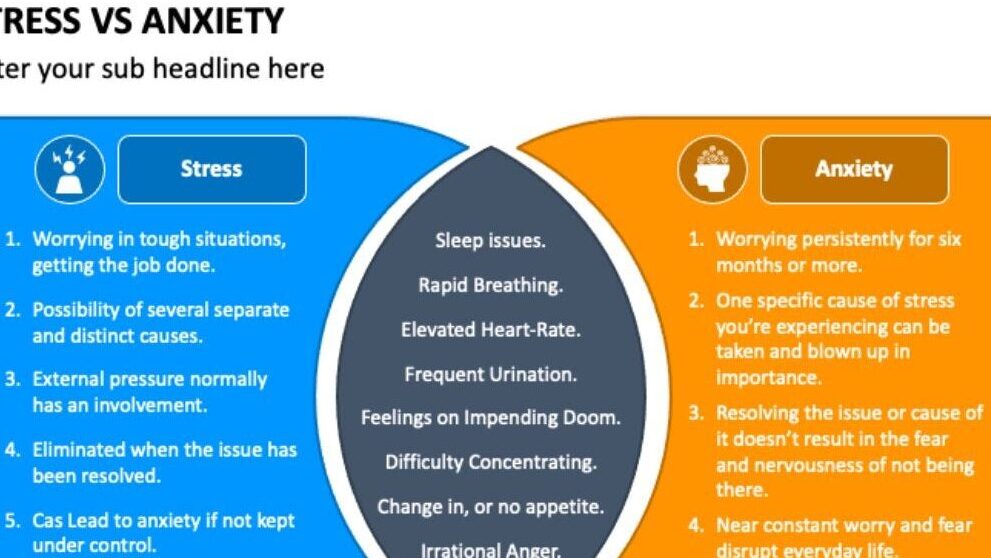
Anxiety and stress are two commonly experienced emotions that can have a significant impact on our mental and physical well-being. While they often go hand-in-hand, it is important to recognize that they are distinct experiences with different underlying causes and manifestations.
Anxiety refers to a state of excessive worry, fear, and apprehension that is often accompanied by physical symptoms such as racing heart, sweaty palms, and difficulty concentrating. It is generally characterized by persistent and uncontrollable thoughts that are focused on potential future threats or dangers. Anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, involve more intense and prolonged feelings of anxiety that can significantly interfere with daily functioning.
On the other hand, stress is a response to a specific external event or situation that is perceived as a threat or challenge. It is usually temporary and subsides once the stressor is removed or resolved. Stress can be caused by a variety of factors, including work-related pressures, financial difficulties, relationship problems, or major life changes. While some level of stress is normal and can even be beneficial in certain situations, chronic or excessive stress can lead to negative health outcomes and contribute to the development of anxiety or other mental health disorders.
Understanding the differences between anxiety and stress can help individuals better identify and address their emotional experiences. By seeking appropriate support and implementing effective coping strategies, individuals can minimize the impact of these emotional states and improve their overall well-being. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the signs and symptoms of anxiety and stress, exploring their effects on mental and physical health, and discussing strategies for managing and preventing their detrimental effects.
The Impact of Anxiety and Stress on Mental and Physical Health
Excessive anxiety and stress can have profound effects on both mental and physical health. The mind and body are intricately connected, and when one suffers, the other is often affected as well. In terms of mental health, chronic anxiety and stress can lead to the development or exacerbation of various psychiatric disorders, such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Persistent feelings of worry, fear, and unease can significantly impair one’s ability to function and enjoy daily life, leading to social isolation, poor self-esteem, and decreased productivity.
The impact of anxiety and stress on physical health is equally significant. The body reacts to stress by releasing stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can have detrimental effects on various bodily systems. Chronic stress has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. The immune system also suffers, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Additionally, prolonged anxiety and stress can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep disorders like insomnia, further compromising overall well-being.
It is crucial to recognize the far-reaching consequences of anxiety and stress on both mental and physical health. Understanding the interconnectedness of the mind and body can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing and preventing these issues. With effective coping mechanisms and strategies, it is possible to limit the detrimental effects of anxiety and stress, promoting a healthier and more balanced life.
Common Causes of Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress are two common experiences that many individuals face in their daily lives. While they can be triggered by a variety of factors and vary from person to person, there are several common causes that contribute to these feelings of unease and tension.
One of the primary causes of anxiety and stress is work-related pressures. The demanding nature of our jobs, excessive workload, tight deadlines, and the fear of failure can all lead to heightened levels of anxiety and stress. In fact, a study conducted by the American Psychological Association found that nearly 60% of adults identified work as a significant source of stress in their lives.
Another common cause is financial worries. Money plays an integral role in our lives and can be a significant source of anxiety and stress. Whether it’s struggling to make ends meet, mounting debt, or the fear of financial instability, these concerns can take a toll on our mental well-being. A report by the National Institute of Mental Health stated that financial stress is a leading cause of anxiety disorders, showing just how pervasive its impact can be.
Relationship issues can also contribute to feelings of anxiety and stress. Whether it’s conflicts in a romantic relationship, difficulties with family members, or strained friendships, the challenges we face in our personal connections can have a significant impact on our mental state. A study published in the Journal of Marital and Family Therapy highlighted the strong correlation between relationship dissatisfaction and symptoms of anxiety and stress.
While these are just a few examples, it is important to recognize that everyone’s experience with anxiety and stress is unique. Identifying the specific causes that contribute to your own feelings of unease is essential in developing effective coping mechanisms and strategies for managing these challenges. By gaining a deeper understanding of what triggers anxiety and stress, we can take proactive steps towards achieving a greater sense of calm and well-being in our lives.
Certainly! Here’s a table summarizing common causes of anxiety and stress:
| Common Causes of Anxiety and Stress | Description |
|---|---|
| Work-related Stress | High Workload: Excessive work demands and tight deadlines. |
| Job Insecurity: Fear of job loss or instability. | |
| Financial Stress | Debt: Overwhelming financial obligations and debt. |
| Unemployment: Job loss or uncertainty about financial stability. | |
| Relationship Issues | Conflict: Strained relationships and unresolved conflicts. |
| Breakups or Divorce: Endings of significant relationships. | |
| Health Concerns | Chronic Illness: Managing or coping with chronic health conditions. |
| Acute Health Events: Sudden illnesses or medical emergencies. | |
| Life Transitions | Major Life Changes: Significant events like moving, marriage, or having a child. |
| Retirement: Adjusting to life changes after retirement. | |
| Uncertainty about the Future | Ambiguity: Lack of clarity or uncertainty about future events. |
| Career Path: Uncertainty about career direction or goals. | |
| Social Pressures | Social Expectations: Pressure to meet societal expectations. |
| Social Comparison: Comparing oneself unfavorably to others. | |
| Academic Pressure | Exams and Assignments: Pressure related to academic performance. |
| Educational Transitions: Moving from one educational level to another. | |
| Technology and Information Overload | Constant Connectivity: Always being connected and overwhelmed by information. |
| Media Influence: Exposure to negative news and social media stressors. | |
| Traumatic Events | Personal Trauma: Experiencing or witnessing traumatic events. |
| Natural Disasters: Impact of earthquakes, floods, or other natural disasters. | |
| Lack of Work-life Balance | Long Working Hours: Difficulty in balancing work and personal life. |
| Burnout: Feeling emotionally drained and exhausted from work. | |
| Environmental Factors | Noise and Pollution: Environmental stressors affecting well-being. |
| Living Conditions: Uncomfortable or challenging living situations. | |
| Family Expectations and Responsibilities | Parental Expectations: Pressure to meet family expectations and responsibilities. |
| Caregiver Stress: Caring for aging parents or family members. | |
| Personal Expectations and Perfectionism | Self-imposed Pressure: Setting high standards and fearing failure. |
| Perfectionism: Striving for unattainable perfection in various aspects of life. |
Developing Coping Mechanisms for Anxiety and Stress
Stress and anxiety are common experiences in today’s fast-paced world, affecting millions of people worldwide. It is crucial to develop effective coping mechanisms to alleviate these burdens and restore a sense of balance and well-being. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, there are several strategies that can help individuals manage and cope with anxiety and stress more effectively.
One of the most effective coping mechanisms for anxiety and stress is practicing relaxation techniques. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help calm the mind and body, reducing feelings of anxiety and stress. These techniques work by activating the body’s relaxation response, which counters the effects of the stress response, promoting a sense of calmness and tranquility.
Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to be a powerful coping mechanism for anxiety and stress. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters, and helps reduce stress hormones in the body. Whether it’s going for a brisk walk, doing yoga, or hitting the gym, finding an activity that you enjoy and can commit to regularly can have significant benefits for your mental and physical well-being.
Incorporating these coping mechanisms into your daily routine can have a profound impact on your ability to manage anxiety and stress. By utilizing relaxation techniques and engaging in regular physical activity, you can equip yourself with the tools needed to navigate life’s challenges more effectively. Remember, everyone’s experience with anxiety and stress is unique, so it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare professional or therapist to explore additional coping strategies tailored to your specific needs.
Effective Strategies for Managing Anxiety and Stress
Our ability to effectively manage anxiety and stress plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall mental and physical well-being. By incorporating proven strategies into our daily lives, we can empower ourselves to better cope with the challenges that come our way. Here, we explore some effective techniques that can help reduce anxiety and stress levels.
Firstly, practicing relaxation techniques has been shown to have a significant impact on managing anxiety and stress. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help calm the mind and relax the body. Taking just a few minutes each day to engage in these practices can promote a sense of calm and reduce feelings of tension or overwhelm.
Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity into our routines can have a profound effect on anxiety and stress levels. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain. Whether it’s a brisk walk, a yoga session, or a high-intensity workout, finding an activity that suits our preferences and capabilities can provide an outlet for stress and promote a sense of well-being.
Furthermore, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress-reducing activities can significantly contribute to managing anxiety and stress. Consuming nutrient-rich foods, prioritizing quality sleep, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help support our overall mental and physical health. Implementing these habits can bolster our resilience and ability to navigate challenging situations with greater ease.
Incorporating effective strategies for managing anxiety and stress into our lives not only helps us cope in the present but also sets a foundation for long-term well-being. By prioritizing relaxation techniques, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, we can equip ourselves with the tools necessary to navigate life’s stressors more effectively. As we continue on our journey towards optimal well-being, let us remember that self-care and self-compassion are essential components of stress management that deserve our attention and commitment.
Incorporating Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques in Daily Life
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques have proven to be effective ways to reduce anxiety and stress in our daily lives. By incorporating these techniques into our routines, we can create a sense of calm and inner peace.
One powerful method is mindfulness meditation, which involves focusing your attention on the present moment and becoming more aware of your thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations without judgment. Research has shown that regular mindfulness practice can lead to a reduction in anxiety and stress levels, improved emotional well-being, and better overall mental health. Taking a few minutes each day to sit quietly, breathe deeply, and bring your awareness to the present can make a significant difference in your stress levels.
Another effective technique is progressive muscle relaxation, where you systematically tense and release different muscle groups to promote physical and mental relaxation. This method helps to relieve muscle tension, reduce anxiety symptoms, and induce a state of deep relaxation. By progressively tensing and relaxing each muscle group, you can develop a heightened sense of body awareness and alleviate built-up tension and stress. This technique can be done at any time and in any place, making it a convenient and accessible tool for stress management.
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques into your daily life can have profound benefits for your mental and physical well-being. By dedicating some time each day to practice these techniques, you can cultivate a greater sense of calm, reduce anxiety and stress levels, and improve your overall quality of life. So why not give it a try and discover the transformative power of mindfulness and relaxation in your own life?
The Role of Exercise and Physical Activity in Reducing Anxiety and Stress
Regular physical exercise and activity have been proven to play a crucial role in reducing anxiety and stress levels. Engaging in exercise releases endorphins, which are commonly known as “feel-good” chemicals in the brain. These endorphins help to improve mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and stress. In fact, numerous studies have shown that physical activity can be as effective as medication and therapy in managing anxiety and stress.
Exercise also has a positive impact on the body’s physiological response to stress. When we experience stress, our body goes into “flight or fight” mode, releasing stress hormones such as cortisol. Regular physical activity helps to regulate these stress hormones and lowers cortisol levels, leading to a reduction in anxiety and stress. Additionally, exercise promotes better sleep quality, which is important in managing anxiety and stress. Lack of sleep can worsen anxiety symptoms and increase stress levels, while regular exercise can improve sleep patterns and help individuals achieve a more restful and rejuvenating sleep. Overall, incorporating exercise and physical activity into our daily routines can significantly contribute to reducing anxiety and stress, both mentally and physically.
Seeking Professional Help: Therapy and Counseling Options
When it comes to managing anxiety and stress, seeking professional help through therapy and counseling can be an effective and beneficial approach. Therapy and counseling provide individuals with the opportunity to work with trained professionals who specialize in treating mental health conditions, such as anxiety and stress. These professionals, often licensed therapists or counselors, are equipped with the knowledge and expertise to guide individuals through the challenges they are facing and provide the necessary support and tools for managing their symptoms.
Therapy and counseling offer a safe and confidential environment for individuals to express their thoughts and feelings openly. Through various therapeutic techniques and modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), or mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), therapists and counselors help individuals gain insight into their anxiety and stress triggers, develop coping strategies, and improve overall well-being. Additionally, therapy and counseling can also assist in identifying any underlying issues or co-occurring mental health disorders that may be contributing to anxiety and stress.
Working with a therapist or counselor can provide individuals with a personalized and tailored approach to managing anxiety and stress. These professionals can help individuals build resilience, develop healthy coping mechanisms, and learn effective strategies for relaxation and stress reduction. They can also provide ongoing support and guidance throughout the process, helping to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Seeking professional help through therapy and counseling is an essential step towards managing anxiety and stress effectively and improving overall mental health and well-being.
Exploring Medication Options for Anxiety and Stress Management
Medication can be a helpful tool in managing anxiety and stress, particularly for individuals who experience severe symptoms or struggle to find relief through other means. While there are various types of medications available, they should always be prescribed and supervised by a qualified healthcare professional.
One commonly prescribed class of medications for anxiety and stress is benzodiazepines. These medications work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which helps to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Benzodiazepines can be effective in providing short-term relief, but they should be used with caution due to their potential for dependence and side effects such as drowsiness and impaired coordination. Long-term use is generally not recommended, as it can lead to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.
Another class of medications commonly used for anxiety and stress is selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). SSRIs work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood, in the brain. These medications are usually prescribed for longer-term use and are considered safer and less addictive than benzodiazepines. However, it can take several weeks for the full effects of SSRIs to be experienced, and they may cause side effects such as nausea, sexual dysfunction, and weight changes.
In addition to benzodiazepines and SSRIs, other classes of medications, such as beta blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and antipsychotics, may be used in specific cases or in combination with other treatments. The choice and dosage of medication will depend on an individual’s unique circumstances, including their symptoms, medical history, and any concurrent conditions they may have. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to find the most appropriate medication and dosage for effective anxiety and stress management.
The Importance of Healthy Lifestyle Habits in Managing Anxiety and Stress
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing anxiety and stress effectively. Adopting healthy habits can have a positive impact on both our mental and physical well-being, promoting resilience and reducing the risk of developing long-term complications. Research has consistently shown that incorporating regular exercise, following a balanced diet, practicing good sleep hygiene, and engaging in relaxation techniques can significantly alleviate symptoms of anxiety and stress.
Physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, has been found to stimulate the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood enhancers. These endorphins can help reduce feelings of anxiety and stress, leading to an improved overall sense of well-being. The American Psychological Association (APA) recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise to reap the mental health benefits. Additionally, maintaining a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients that support brain function and reduce inflammation, which has been linked to anxiety and stress. Sleep also plays a vital role in managing these conditions, as it allows the body and mind to recharge. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques before bed, and creating a calm sleep environment can help improve the quality and duration of sleep, ultimately reducing the impact of anxiety and stress on our daily lives.
Building a Supportive Network and Seeking Social Connections
Building a supportive network and seeking social connections can play a crucial role in managing anxiety and stress. Humans are social beings by nature, and having strong social connections has been linked to better mental and emotional well-being. When individuals surround themselves with supportive and understanding friends, family, and community, they can find comfort, empathy, and reassurance during challenging times.
Research suggests that social support can help in various ways. For instance, having a support network provides individuals with a safe space to express their feelings and concerns, allowing them to release emotional tension and gain perspective. Moreover, supportive relationships can offer practical assistance, such as help with daily tasks or problem-solving, which can lighten the load and reduce stress.
In addition, interacting with others helps combat feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common in those experiencing anxiety and stress. Social connections can provide a sense of belonging and validation, fostering a positive mindset and improving overall mental health. Sharing experiences with like-minded individuals can also offer a sense of camaraderie and empowerment, reminding individuals that they are not alone in their struggles.
Building a supportive network and seeking social connections may involve reaching out to trusted friends, participating in group activities or hobbies, joining support groups, or seeking professional therapy options. By actively cultivating a network of caring individuals, individuals can create a supportive environment that promotes resilience and enhances their ability to cope with anxiety and stress.
Creating a Balanced Work-Life Routine to Minimize Anxiety and Stress
Maintaining a balanced work-life routine is essential for minimizing anxiety and stress. In today’s fast-paced and demanding world, it can be challenging to find the right equilibrium between professional responsibilities and personal well-being. However, by implementing certain strategies and prioritizing self-care, it is possible to create a harmonious routine that promotes mental and emotional health.
One key aspect of developing a balanced work-life routine is setting clear boundaries between work and personal life. It is vital to establish designated times for work-related activities and stick to them as much as possible. This may involve establishing a specific start and end time for work, dedicating specific days or hours for personal activities and leisure, and avoiding the temptation to constantly check emails or engage in work-related tasks during non-working hours. By doing so, individuals can create a sense of separation and ensure that they allocate sufficient time for relaxation, hobbies, and spending quality time with loved ones.
Long-Term Strategies for Preventing and Managing Anxiety and Stress.
Long-term strategies for preventing and managing anxiety and stress are essential for maintaining mental and emotional well-being. While short-term coping mechanisms may provide temporary relief, it is crucial to adopt practices that promote long-lasting resilience and balance in our lives. Here are two key approaches that can contribute significantly to the prevention and management of anxiety and stress:
1. Cultivating a healthy lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle is the foundation for managing anxiety and stress in the long term. Ensuring a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep can have a profound impact on our overall well-being. Research suggests that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can reduce symptoms of anxiety and stress. Additionally, physical activity has been shown to increase the production of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Prioritizing quality sleep is also crucial, as sleep deprivation can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and stress. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a calm and comfortable bedroom environment can greatly contribute to better sleep quality.
2. Developing effective coping mechanisms: Building a repertoire of effective coping mechanisms is crucial for long-term anxiety and stress management. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness, can help reduce the physiological response to stress and promote a sense of calmness and clarity. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is another valuable approach that can help individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier and more adaptive coping strategies. Additionally, incorporating self-care practices into our daily routines, such as engaging in hobbies, spending time in nature, or practicing gratitude, can enhance emotional resilience and foster a sense of well-being.
Implementing these long-term strategies for preventing and managing anxiety and stress can make a significant difference in our lives. However, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals or mental health experts for personalized advice and guidance. By prioritizing our mental and emotional well-being, we can improve our overall quality of life and build resilience to effectively navigate life’s challenges.
Is anxiety the same as stress?
Anxiety and stress are related but distinct experiences. While stress is a response to external pressure or demands, anxiety refers to a feeling of unease or worry about future events or uncertain situations.
How can I differentiate between anxiety and stress?
Stress often arises from specific events or situations, while anxiety is more generalized and not necessarily tied to a specific trigger. Anxiety may also involve physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, whereas stress often manifests as irritability or difficulty concentrating.
Can anxiety and stress impact my physical health?
Yes, both anxiety and stress can have detrimental effects on your mental and physical well-being. Prolonged anxiety and stress can increase the risk of various health issues, including cardiovascular problems, weakened immune system, and digestive disorders.
Are there any effective coping mechanisms for anxiety and stress?
Yes, there are various coping mechanisms that can help manage anxiety and stress. These include deep breathing exercises, practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies or activities you enjoy, and seeking social support.
Is medication an option for managing anxiety and stress?
In some cases, medication may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to help manage severe anxiety or chronic stress. However, medication should be considered as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that also includes therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
How can exercise and physical activity help reduce anxiety and stress?
Engaging in regular physical activity increases the production of endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers. Exercise also helps reduce muscle tension, promotes better sleep, and provides a healthy outlet for stress and anxiety.
When should I seek professional help for anxiety and stress?
If anxiety and stress are significantly impacting your daily life, relationships, or overall well-being, it is advisable to seek professional help. A therapist or counselor can provide guidance, support, and effective strategies to manage anxiety and stress.
How important are healthy lifestyle habits in managing anxiety and stress?
Healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding excessive consumption of alcohol or caffeine, play a crucial role in managing anxiety and stress. These habits help support overall mental and physical well-being.
How can I build a supportive network and seek social connections to manage anxiety and stress?
Building a supportive network involves seeking out positive relationships, whether with friends, family, or support groups. Sharing your experiences, concerns, and emotions with trusted individuals can help alleviate anxiety and stress.
What are some strategies for creating a balanced work-life routine to minimize anxiety and stress?
To create a balanced work-life routine, it’s important to set boundaries, prioritize self-care, and schedule time for relaxation and hobbies. Finding a healthy work-life balance helps prevent burnout and reduces anxiety and stress levels.
What are some long-term strategies for preventing and managing anxiety and stress?
Long-term strategies include incorporating stress management techniques into daily life, such as mindfulness practices, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, seeking professional help when needed, and building a strong support network. These strategies help prevent and effectively manage anxiety and stress over time.






