Hormones and Prostate Diseases: What’s the Connection and How to Manage It

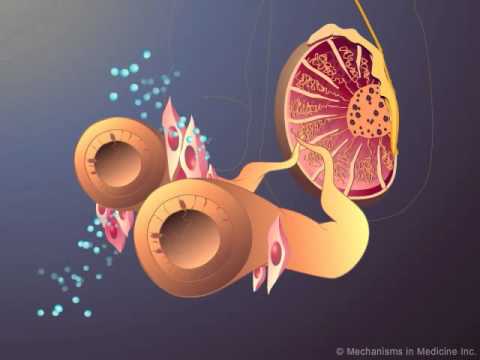
Understanding the Prostate: A Brief Overview

The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ that plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. Located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum, it surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The primary function of the prostate is to produce a fluid that forms part of semen, which nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation.
Although the prostate is an essential part of the male reproductive system, it is prone to various diseases and conditions. Some common prostate diseases include prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate inflammation or prostatitis, and prostate cancer. These conditions can cause a range of symptoms, including difficulty urinating, frequent urination, weak urine flow, and pain or discomfort in the pelvic area. Understanding the prostate and the potential issues it may face is crucial for maintaining optimal prostate health.
Common Prostate Diseases and their Symptoms
Prostate diseases, unfortunately, are quite common in men, especially as they age. These diseases can cause significant discomfort and affect various aspects of a man’s quality of life. Let’s explore some of the most common prostate diseases and their symptoms.
One of the most prevalent prostate diseases is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BPH occurs when the prostate gland enlarges and begins to press against the urethra, causing urinary symptoms. Men with BPH may experience frequent urination, urgency to urinate, weak urine flow, difficulty starting or stopping urination, and the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. While BPH is not cancerous, it can still cause bothersome symptoms that require medical attention.
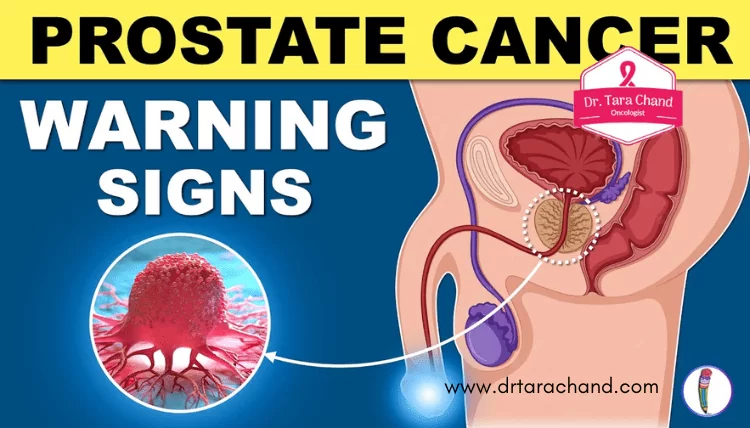
Another significant prostate disease is prostate cancer, which occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate gland start to grow uncontrollably. Prostate cancer often develops slowly and may not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, men may experience symptoms such as difficulty urinating, blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, and even bone pain if the cancer spreads to other parts of the body. Early detection through regular screening is vital for effective management and improved outcomes.
It is important to remember that these symptoms can vary from person to person, and their presence does not necessarily indicate the presence of a prostate disease. If you or someone you know experiences any concerning symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Role of Hormones in Prostate Health

The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder and surrounding the urethra in men. It plays a vital role in the reproductive system by producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. Hormones, especially testosterone and estrogen, are essential for the development and maintenance of prostate health.
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for the growth and maturation of the prostate gland. It stimulates the cell growth, function, and overall maintenance of the gland. However, an imbalance in testosterone levels can contribute to the development of certain prostate diseases. Estrogen, usually considered a female hormone, is also present in men but in smaller amounts. It is involved in regulating the growth and function of the prostate gland. An imbalance in estrogen levels, such as an increase relative to testosterone, can also impact prostate health. Understanding the role of hormones in prostate health is crucial for diagnosing, treating, and managing prostate diseases effectively.
• Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for the growth and maturation of the prostate gland.
• It stimulates cell growth, function, and overall maintenance of the gland.
• Imbalance in testosterone levels can contribute to the development of certain prostate diseases.
• Estrogen, usually considered a female hormone, is also present in men but in smaller amounts.
• It regulates the growth and function of the prostate gland.
• An imbalance in estrogen levels relative to testosterone can impact prostate health.
Understanding these hormonal roles allows for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management of prostate diseases.
The Link between Hormones and Prostate Diseases
Hormones play a significant role in the development and progression of prostate diseases. The delicate balance of hormones in the body can greatly influence the health of the prostate gland. Testosterone, the primary male hormone, has been closely linked to the development of prostate diseases such as prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Research suggests that high levels of testosterone may increase the risk of developing these conditions, while low levels may offer some protective benefits. However, the relationship between testosterone and prostate diseases is complex and still not fully understood.
Another hormone that has been implicated in prostate diseases is estrogen. While estrogen is typically considered a female hormone, men also have small amounts of it in their bodies. Estrogen has been found to influence the growth and function of the prostate gland. Studies have shown that high estrogen levels in men may contribute to the development of BPH and prostate cancer. This suggests that hormonal imbalances, not limited to testosterone alone, can have a direct impact on the risk and progression of prostate diseases. Understanding the interplay between these hormones is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of prostate health and disease.
Certainly! Here’s a short data table on the link between hormones and prostate diseases:
| Hormones and Prostate Diseases | Key Concepts | Credible Source |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone and Prostate Growth | – Key Concept: Testosterone, a male sex hormone, plays a role in normal prostate growth, but excessive levels may contribute to prostate issues. | Harvard Health Publishing – Testosterone and the Prostate |
| – Considerations: Maintaining a balance in testosterone levels is crucial for prostate health. | ||
| Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) | – Key Concept: DHT, a derivative of testosterone, is linked to prostate enlargement and may contribute to conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – Prostate Enlargement |
| – Considerations: Understanding DHT’s role helps address issues related to prostate enlargement. | ||
| Estrogen in Prostate Health | – Key Concept: While estrogen is traditionally associated with females, it also plays a role in male prostate health, influencing cell growth and function. | International Journal of Molecular Sciences – Estrogen and Prostate Health |
| – Considerations: Maintaining a balance between estrogen and testosterone is vital for optimal prostate function. | ||
| Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer | – Key Concept: Hormone therapy, such as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), is used to reduce testosterone levels and slow the growth of prostate cancer cells. | American Cancer Society – Hormone Therapy |
| – Considerations: Hormone therapy is a common approach in managing advanced prostate cancer. | ||
| Hormones and Prostate Diseases Research | – Key Concept: Ongoing research explores the intricate relationship between hormones and various prostate diseases, contributing to evolving treatment approaches. | European Urology – Hormonal Manipulation in Prostate Cancer |
| – Considerations: Research advancements provide insights into targeted therapies for prostate diseases. |
Exploring the Impact of Testosterone on Prostate Health
Testosterone, a hormone primarily produced in the testicles, plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of the male reproductive system. It is also known to have a significant impact on prostate health. Testosterone is involved in various processes within the prostate gland, including the regulation of cell growth and differentiation. However, imbalances in testosterone levels can lead to adverse effects on prostate health.
Research suggests that high levels of testosterone in the prostate can stimulate the growth of prostate cells, potentially increasing the risk of prostate diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer. On the other hand, low levels of testosterone have been associated with the development of certain prostate diseases as well. It is important to note that while testosterone is involved in the growth of prostate cells, it is not the sole factor in the development of prostate diseases. Other factors, such as genetics and lifestyle, also play a significant role.
Understanding the impact of testosterone on prostate health is crucial for early detection and prevention of prostate diseases. Regular check-ups, including prostate specific antigen (PSA) tests, can help monitor testosterone levels and identify any potential issues. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can help maintain hormonal balance and support prostate health. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, men can take control of their prostate health and reduce the risk of developing prostate diseases.
Estrogen and its Effects on Prostate Diseases
Estrogen, primarily known as a female hormone, also plays a significant role in the male body. In men, estrogen is produced in small amounts by the testes and adrenal glands. While its levels are much lower compared to females, estrogen still affects various aspects of male health, including the prostate gland.
One of the key effects of estrogen on the prostate is its influence on the growth and development of prostate tissue. Studies have shown that an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone, the primary male hormone, can lead to the excessive growth of prostate cells. This imbalance is often linked to conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. Elevated levels of estrogen, along with a decrease in testosterone, may contribute to the enlargement of the prostate gland and the development of prostate diseases.
The interaction between estrogen and the prostate is complex and requires further investigation to fully understand its mechanisms and implications. However, it is evident that maintaining a balance between estrogen and testosterone is essential for prostate health. Taking steps to regulate estrogen levels and promote hormonal balance may have significant implications in the prevention and management of prostate diseases. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the topic of hormonal imbalances and their contribution to prostate diseases, as well as explore various approaches to support prostate health.
How Hormonal Imbalances Contribute to Prostate Diseases
Hormonal imbalances can play a significant role in the development of prostate diseases. One key hormone that affects the prostate is testosterone. Testosterone is produced primarily in the testes and is responsible for the growth and function of the prostate gland. However, an excess of testosterone can lead to the growth of abnormal cells in the prostate, potentially leading to conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer.
In addition to testosterone, estrogen also has an impact on prostate health. While estrogen is typically associated with female reproductive health, men also produce small amounts of this hormone. Imbalances in estrogen levels can contribute to the development of prostate diseases such as BPH or prostate cancer. Research suggests that elevated estrogen levels can stimulate the growth of prostate cells, leading to the enlargement or malignancy of the prostate gland.
Understanding the intricate relationship between hormones and prostate diseases is crucial in order to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. By identifying and addressing hormonal imbalances, healthcare professionals can potentially reduce the risk or progression of prostate diseases. Further research is needed to uncover the precise mechanisms by which hormonal imbalances contribute to these conditions, but current evidence highlights the importance of maintaining a hormonal balance for optimal prostate health.
The Role of Age in Hormonal Changes and Prostate Health
As men age, the hormonal changes that occur in their bodies can have a significant impact on their prostate health. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in the development and function of the prostate gland. However, as men get older, the production of testosterone naturally declines, leading to hormonal imbalances that can affect prostate health.
Research has shown that a decrease in testosterone levels, also known as hypogonadism, is associated with an increased risk of developing prostate diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. This decrease in testosterone can result in an enlarged prostate, leading to urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty emptying the bladder.
Age-related hormonal changes also involve an increase in estrogen levels, which further contributes to prostate health issues. Studies have found that higher levels of estrogen in the prostate can stimulate the growth of prostate cells and increase the risk of developing prostate diseases. Additionally, estrogen has been linked to inflammation and oxidative stress in the prostate, both of which can damage the gland and contribute to prostate diseases.
Understanding the role of age in hormonal changes and their impact on prostate health is essential for early detection, prevention, and management of prostate diseases. By recognizing the changes that occur with age and the potential risks associated with hormonal imbalances, men can take proactive steps to support their prostate health and reduce the incidence of prostate diseases.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Prostate Diseases
Recognizing the early signs of prostate diseases is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. As with many health conditions, early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and a better quality of life. It is important for individuals, especially those at higher risk, to be aware of the potential warning signs and seek medical attention if they experience any of the following symptoms:
1. Urinary issues: Changes in urination patterns can be an indicator of prostate diseases. Symptoms may include frequent urination, especially at night, a weak or interrupted urine flow, difficulty starting or stopping urination, or the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
2. Blood in urine or semen: The presence of blood in urine or semen, also known as hematuria or hematospermia, respectively, should not be ignored. While these symptoms may not always be indicative of a serious condition, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation to rule out any underlying prostate-related issues.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important not to panic but to make an appointment with your healthcare provider for a comprehensive assessment. They will be able to evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and provide appropriate guidance based on your individual circumstances. Remember, early detection and prompt treatment can play a critical role in effectively managing prostate diseases and ensuring a healthier future.
Diagnostic Tests for Prostate Diseases and Hormonal Imbalances
Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in identifying and diagnosing prostate diseases and hormonal imbalances. These tests help healthcare professionals understand the underlying causes and determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their patients. One commonly used diagnostic test is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test.
The PSA test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland, in a man’s blood. Elevated PSA levels may indicate the presence of prostate diseases such as prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or prostatitis. However, it is important to note that a high PSA level does not necessarily indicate prostate cancer. Further diagnostic tests, such as a digital rectal examination (DRE) and prostate biopsy, may be required to confirm the diagnosis. These additional tests help healthcare professionals gather more information about the size, shape, and texture of the prostate, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
In addition to the PSA test, imaging tests like ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans may be used to provide detailed images of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. These imaging techniques help visualize any abnormalities, such as tumors or inflammation, that may be contributing to the symptoms. Furthermore, hormone level tests, including testosterone and estrogen, can be conducted to assess hormonal imbalances that may be linked to prostate diseases. By analyzing the hormone levels, healthcare professionals can gain insights into the potential causes of the diseases and develop targeted treatment strategies.
By combining the results of these diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose and assess the severity of prostate diseases and hormonal imbalances. This comprehensive approach allows for personalized treatment plans that address the specific needs of each patient. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in prostate health to undergo the necessary diagnostic tests and receive appropriate guidance and treatment.
Hormone Replacement Therapy for Managing Prostate Diseases
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often considered as an option for managing certain prostate diseases. HRT involves the use of hormones, such as testosterone, to replace or supplement the body’s natural hormone levels. This therapy aims to restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms associated with prostate diseases.
There are different forms of hormone replacement therapy available, including oral medications, transdermal patches, injections, and implants. The choice of treatment method depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history, preferences, and the specific prostate disease being treated. It is important to note that hormone replacement therapy should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional, as it can have potential side effects and risks that need to be carefully considered.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Prostate Health
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in supporting prostate health. Making simple changes to your daily routine can have a significant impact on reducing the risk of prostate diseases and promoting overall well-being. One important lifestyle modification is maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Several studies have shown that obesity is associated with an increased risk of prostate diseases, including prostate cancer. Engaging in moderate-intensity activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week can help to maintain a healthy weight and improve prostate health.
In addition to exercise, dietary choices also play a pivotal role in supporting prostate health. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that may help protect against prostate diseases. Incorporating foods like tomatoes, broccoli, green tea, and nuts, which are known for their prostate-protective properties, can be beneficial. It is important to limit the intake of red and processed meats, as they have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Furthermore, reducing the consumption of sugary drinks and high-fat foods can contribute to maintaining a healthy prostate. Making these dietary modifications can go a long way in safeguarding prostate health and ensuring overall well-being.
Dietary Approaches to Reduce the Risk of Prostate Diseases
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of prostate diseases. Including a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet is essential as they are rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Some specific fruits and vegetables that have been linked to a reduced risk of prostate diseases include tomatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, berries, and citrus fruits.
Furthermore, it is important to consume foods that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties and may help lower the risk of prostate diseases. On the other hand, it is recommended to limit the intake of saturated fats and trans fats, which are commonly found in processed foods, red meat, and high-fat dairy products. High consumption of these fats has been associated with an increased risk of prostate diseases.
In addition to a well-balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial for prostate health. Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of prostate diseases, including prostate cancer. To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, it is important to follow a calorie-controlled diet and engage in regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities at least twice a week. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary and lifestyle recommendations based on your individual needs.
Holistic Approaches for Managing Hormones and Prostate Diseases
Holistic approaches offer a complementary approach to managing hormones and prostate diseases. These approaches aim to address the underlying causes of hormonal imbalances and promote overall prostate health through natural therapies and lifestyle modifications.
One holistic approach is the use of herbal remedies and supplements. Some herbs, such as saw palmetto and stinging nettle root, have shown promising results in improving urinary symptoms associated with prostate diseases. These herbs are believed to work by inhibiting the production of certain hormones that contribute to the enlargement of the prostate gland. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any herbal remedy or supplement to ensure safety and efficacy.
In addition to herbal remedies, dietary modifications can also play a role in supporting prostate health. Studies have shown that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, such as those found in fish and olive oil, may help reduce the risk of prostate diseases. On the other hand, consuming a high-fat diet, particularly one that is high in saturated fats, may increase the risk of developing prostate diseases. Therefore, adopting a balanced and nutrient-dense diet is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and optimal prostate health.
Furthermore, stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation and yoga, can also be beneficial for managing hormones and prostate diseases. Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to the development of various health conditions, including prostate diseases. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques into daily life can help regulate hormone levels and promote overall well-being.
While holistic approaches can provide valuable support in managing hormones and prostate diseases, it is important to remember that they should not replace conventional medical treatments. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan that combines both conventional and holistic approaches for optimal results. By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of hormone balance and prostate health, holistic approaches can play a valuable role in promoting overall well-being.
What is the prostate and why is it important?
The prostate is a small gland located in the male reproductive system. It plays a crucial role in producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
What are some common prostate diseases and their symptoms?
Common prostate diseases include prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and prostatitis. Symptoms of these diseases may include difficulty urinating, frequent urination, blood in the urine or semen, pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, and erectile dysfunction.
How do hormones affect prostate health?
Hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen, have a significant impact on prostate health. Imbalances in these hormones can contribute to the development and progression of prostate diseases.
What is the relationship between testosterone and prostate health?
Testosterone is a key hormone involved in prostate health. While it is necessary for normal prostate function, high levels of testosterone or its conversion to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can increase the risk of prostate enlargement and cancer.
How does estrogen affect prostate diseases?
Although estrogen is predominantly a female hormone, men also have small amounts of it. Elevated levels of estrogen in men have been linked to an increased risk of prostate diseases, including prostate cancer.
How do hormonal imbalances contribute to prostate diseases?
Hormonal imbalances, such as an excess of testosterone or estrogen, can disrupt the normal functioning of the prostate gland and contribute to the development of prostate diseases.
Does age play a role in hormonal changes and prostate health?
Yes, as men age, their hormone levels naturally change. The decline in testosterone and increase in estrogen with age can affect prostate health and potentially contribute to the development of prostate diseases.
What are the early signs of prostate diseases?
The early signs of prostate diseases may include urinary difficulties, such as weak urine flow or increased frequency of urination, blood in the urine or semen, pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, and erectile dysfunction. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if any of these symptoms are experienced.
What are the diagnostic tests for prostate diseases and hormonal imbalances?
Diagnostic tests for prostate diseases may include a digital rectal exam (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, biopsy, and imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI. Hormonal imbalances can be assessed through blood tests to measure hormone levels.
Can hormone replacement therapy help manage prostate diseases?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be used in some cases to manage prostate diseases by restoring hormonal balance. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if HRT is suitable and safe for individual circumstances.
Are there any lifestyle modifications that can support prostate health?
Yes, certain lifestyle modifications can support prostate health. These may include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and practicing good hygiene.
Are there any dietary approaches to reduce the risk of prostate diseases?
Yes, a healthy diet can help reduce the risk of prostate diseases. Including foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, and legumes, as well as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, can be beneficial. Limiting red meat and processed food intake is also recommended.
Are there any holistic approaches for managing hormones and prostate diseases?
Yes, holistic approaches for managing hormones and prostate diseases include natural remedies like herbal supplements, acupuncture, stress reduction techniques, and lifestyle modifications. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any holistic approaches to ensure safety and effectiveness.