How to Prevent Anxiety Attacks: Signs, Triggers, and Coping Techniques

Understanding the Nature of Anxiety Attacks
Anxiety attacks can be frightening and overwhelming experiences that often leave individuals feeling helpless and exhausted. Understanding the nature of anxiety attacks is crucial in order to effectively manage and prevent them. Anxiety attacks, also referred to as panic attacks, are characterized by sudden and intense feelings of fear or distress. These episodes can occur seemingly out of nowhere and can last for a few minutes to several hours.
During an anxiety attack, individuals may experience a variety of physical symptoms including rapid heartbeat, chest tightness, shortness of breath, dizziness, and sweating. These physical sensations can be incredibly distressing and can mimic symptoms of a heart attack or other medical conditions. It’s important to note that anxiety attacks are not life-threatening, although they can certainly feel that way in the moment.
In addition to physical symptoms, anxiety attacks can also manifest in emotional signs such as a sense of impending doom, intense fear, or a feeling of being detached from oneself or reality. These emotional experiences can further exacerbate the distress caused by the physical symptoms. Understanding the emotional signs of anxiety attacks is essential in order to differentiate these episodes from other mental health conditions and provide appropriate support and treatment.
Overall, understanding the nature of anxiety attacks involves recognizing the physical symptoms and emotional signs that accompany these episodes. By gaining a better understanding of these experiences, individuals can work towards developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate professional help when necessary.
Recognizing the Physical Symptoms of Anxiety Attacks
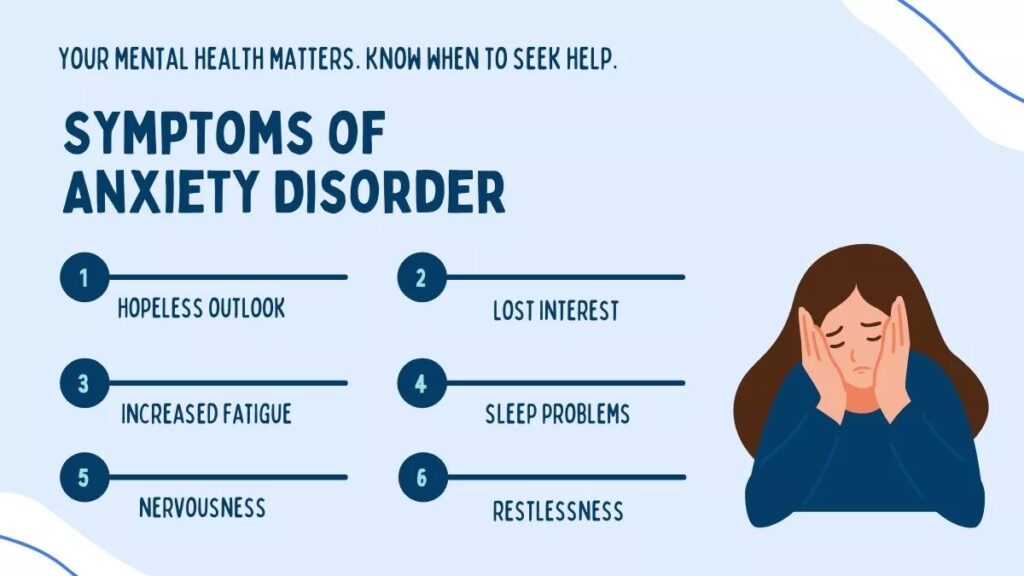
Physical symptoms of anxiety attacks can vary from person to person, but there are some common signs to look out for. One of the most noticeable physical symptoms is a rapid heartbeat. During an anxiety attack, the body’s fight-or-flight response is triggered, causing the heart to beat faster in preparation for danger. This can feel like your heart is racing or pounding in your chest, and it can be quite distressing.
Another physical symptom of anxiety attacks is shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. When we feel anxious, our breathing pattern can become shallow and rapid, leading to a sensation of not being able to get enough air. This can be accompanied by chest tightness or a feeling of being suffocated. It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be signs of other medical conditions, so if you experience them it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying causes.
Identifying the Emotional Signs of Anxiety Attacks

Anxiety attacks can manifest in a variety of ways, and one common avenue through which they can be identified is by examining the emotional signs. These emotional signs can often be intense and overwhelming, and may include feelings of fear, apprehension, or a sense of impending doom. People experiencing an anxiety attack may also find themselves feeling easily irritable or agitated, with their emotions fluctuating rapidly. It is important to note that these emotional signs can vary from person to person, so it’s crucial to consider the individual’s unique emotional experience when trying to identify an anxiety attack.
Another emotional sign that may indicate an anxiety attack is the presence of excessive worry or excessive concern about everyday activities or upcoming events. These worries are often disproportionate to the actual circumstances, and can lead to a sense of restlessness or an inability to relax. Additionally, individuals experiencing an anxiety attack may also struggle with a nagging sense of unease or a racing mind, which can make it difficult for them to concentrate or focus on tasks at hand. It is important to recognize such emotional signs as they can play a crucial role in identifying an anxiety attack and can serve as a starting point for seeking appropriate support and treatment.
Uncovering the Common Triggers for Anxiety Attacks
Anxiety attacks can occur suddenly and unpredictably, leaving individuals feeling overwhelmed and distressed. Identifying the common triggers for anxiety attacks is crucial in managing and preventing these episodes. While the triggers can vary from person to person, there are several recurring factors that tend to contribute to anxiety attacks.
One common trigger is stress. High levels of stress, whether it stems from work, relationships, or personal challenges, can overload the body’s stress response system, leading to anxiety attacks. It’s essential to identify sources of stress in one’s life and develop effective coping strategies to mitigate their impact.
Another significant trigger is certain phobias or fears. Whether it’s a fear of heights, spiders, or public speaking, these specific triggers can set off episodes of anxiety. It’s essential to pinpoint these fears and explore therapeutic approaches, such as exposure therapy, to gradually overcome them.
Additionally, traumatic experiences can act as powerful triggers for anxiety attacks. Witnessing or experiencing a traumatic event can have a lasting impact on an individual’s mental well-being. Understanding and addressing the underlying trauma through therapy or counseling can help manage anxiety attacks associated with these triggers.
Certain medications and substances can also contribute to anxiety attacks. Stimulants like caffeine or nicotine, for example, can heighten anxiety symptoms. It’s crucial to be aware of the potential effects of these substances and make informed choices to reduce their impact.
Uncovering the common triggers for anxiety attacks is a crucial step in managing this debilitating condition. By identifying stressors, fears, traumas, and substances that may contribute to anxiety, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent and alleviate these distressing episodes. Seeking professional support from therapists, psychologists, or counselors can provide guidance and strategies for effectively coping with anxiety triggers.
Certainly! Here’s a table summarizing common triggers for anxiety attacks and strategies to uncover and manage them:
| Uncovering Common Triggers for Anxiety Attacks | Description |
|---|---|
| Identifying Specific Situations | Recognizing Triggers: Identifying specific situations or environments that consistently trigger anxiety attacks. |
| Journaling: Keeping a journal to track circumstances, emotions, and thoughts preceding anxiety episodes. | |
| Understanding Internal Triggers | Negative Self-Talk: Identifying negative self-talk and irrational thoughts that contribute to anxiety attacks. |
| Body Sensations: Recognizing physical sensations or cues within the body that signal the onset of anxiety. | |
| Social and Performance-Related Triggers | Social Interactions: Uncovering anxiety triggers related to social situations, gatherings, or performance expectations. |
| Public Speaking: Identifying fears associated with public speaking or being in the spotlight as potential triggers. | |
| Cognitive and Catastrophic Thinking Patterns | Cognitive Distortions: Recognizing cognitive distortions such as catastrophizing or expecting the worst-case scenario. |
| Pattern Recognition: Identifying recurring thought patterns that escalate into anxiety attacks. | |
| Past Trauma and Emotional Triggers | Traumatic Experiences: Addressing past traumas or emotional triggers that may resurface and contribute to anxiety attacks. |
| Therapeutic Exploration: Seeking professional help to explore and process past traumas and their impact on anxiety. | |
| Stressful Life Events and Daily Hassles | Life Changes: Recognizing how major life events or daily stressors contribute to heightened anxiety. |
| Stress Management: Implementing stress management techniques to address ongoing stressors and prevent anxiety attacks. | |
| Health-Related Concerns and Anxiety | Health Anxiety: Addressing concerns about health or illness that may be contributing to anxiety attacks. |
| Medical Consultation: Seeking reassurance and guidance from healthcare professionals regarding health-related worries. | |
| Environmental Triggers | Overstimulation: Identifying triggers related to sensory overload, such as loud noises, bright lights, or crowded spaces. |
| Creating Safe Spaces: Designating calm and safe environments to retreat to during periods of heightened anxiety. | |
| Unhealthy Lifestyle Factors | Sleep Deprivation: Recognizing the impact of inadequate sleep on anxiety levels and the occurrence of anxiety attacks. |
| Diet and Nutrition: Exploring the connection between diet, caffeine intake, and the exacerbation of anxiety symptoms. | |
| Interoceptive and Hypervigilance Triggers | Focused Attention: Recognizing triggers related to heightened interoceptive awareness and hypervigilance. |
| Mindfulness Practices: Implementing mindfulness techniques to manage interoceptive sensations and promote relaxation. | |
| Personal Relationships and Boundaries | Conflict and Boundaries: Identifying relationship dynamics or difficulties with setting boundaries as potential triggers. |
| Communication Skills: Improving communication and assertiveness skills to address relationship-related anxiety triggers. | |
| Substance Use and Withdrawal | Substance-Related Triggers: Recognizing the impact of substance use or withdrawal on anxiety levels. |
| Seeking Support: Consulting professionals or support groups for assistance in managing substance-related triggers. | |
| Self-Reflective Practices | Mindful Self-Reflection: Engaging in self-reflective practices to gain insights into personal triggers and coping strategies. |
| Therapeutic Support: Seeking guidance from therapists or counselors to navigate self-discovery and trigger management. |
Exploring the Relationship Between Anxiety and Stress
The relationship between anxiety and stress is complex and often intertwined. While stress is a natural and inevitable part of life, excessive or chronic stress can lead to the development or exacerbation of anxiety disorders. Anxiety, on the other hand, can contribute to increased stress levels, creating a cyclical pattern that can be challenging to break.
When we experience stress, our bodies release stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare us for a “fight or flight” response. While these hormones can be beneficial in short-term stressful situations, prolonged exposure to stress can lead to an overactive stress response system. This can heighten our sensitivity to stressors and increase the likelihood of anxiety symptoms.
Research has shown that individuals with chronic stress are more likely to experience anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or panic disorder. In fact, studies have found that prolonged stress can result in alterations in brain structure and function, particularly in areas associated with fear and anxiety responses.
Additionally, individuals with anxiety disorders may have a heightened stress response to everyday stressors, making it more difficult for them to cope with stress in a healthy manner. This can further perpetuate the cycle of anxiety and stress, leading to a continuous state of heightened arousal and emotional distress.
Understanding the relationship between anxiety and stress is crucial for effective management and prevention. By implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as regular exercise, relaxation techniques, and proper self-care, individuals can help alleviate both stress and anxiety symptoms. It is also important to seek professional help if anxiety symptoms become disruptive to daily life or if stressors are consistently overwhelming. With the right support and tools, it is possible to break the cycle of anxiety and stress and lead a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Examining the Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Anxiety Attacks
Several lifestyle factors have been found to have a significant impact on anxiety attacks. First and foremost, high levels of stress can greatly contribute to the occurrence and severity of anxiety attacks. Chronic stressors such as work pressure, relationship problems, or financial difficulties can cause ongoing anxiety and increase the likelihood of experiencing an attack. Studies have shown that individuals who experience high levels of stress are more prone to anxiety and panic disorders.
In addition to stress, inadequate sleep and poor sleep quality have been linked to a higher risk of anxiety attacks. Lack of sleep can disrupt the body’s natural processes, including the regulation of stress hormones and neurotransmitters. As a result, individuals who consistently experience sleep disturbances may be more susceptible to anxiety attacks. It is essential to prioritize sleep hygiene and establish a regular sleep routine to minimize the impact of sleep deprivation on anxiety.
Strategies for Managing Anxiety Attacks in the Workplace
Strategies for Managing Anxiety Attacks in the Workplace
When it comes to managing anxiety attacks in the workplace, it’s important to prioritize self-care and create a supportive environment. One effective strategy is to practice stress-reducing techniques during breaks or downtime. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can all help calm the mind and body, reducing the frequency and intensity of anxiety attacks.
Creating a workspace that promotes relaxation and focus can also make a significant difference. Consider placing a small plant on your desk, as studies have shown that nature can have a calming effect on stress levels. Additionally, organizing your workspace and minimizing clutter can improve productivity and reduce feelings of overwhelm. Taking regular breaks, even if it’s just a short walk around the office or a few minutes of stretching, can help relieve tension and improve overall well-being. By implementing these strategies, individuals can better manage their anxiety attacks and cultivate a more balanced and positive work environment.
Nurturing Healthy Relationships to Prevent Anxiety Attacks
Building and nurturing healthy relationships can play a significant role in preventing anxiety attacks. When we have a strong support system of loved ones who understand and empathize with our struggles, it can greatly reduce the feelings of isolation and stress that often contribute to anxiety. Healthy relationships provide a safe space for us to express our emotions, seek advice, and receive the support we need.
Research has shown that individuals with strong social support networks are better equipped to manage anxiety and cope with the challenges it presents. Having someone to talk to, whether it’s a partner, family member, or close friend, can be incredibly beneficial in times of distress. Being able to share our fears and worries with a trusted confidant can help to alleviate anxiety and provide a fresh perspective on our concerns.
Additionally, nurturing healthy relationships involves open and effective communication. It’s important to express our emotions and needs to those around us, as this can foster understanding and empathy. Sharing our experiences with anxiety can help our loved ones to better comprehend the impact it has on our lives and enable them to offer the support and encouragement we require.
In conclusion, fostering healthy relationships is crucial in preventing anxiety attacks. These connections provide us with a sense of belonging, emotional support, and a safe space to express our concerns. By prioritizing and nurturing our relationships, we can create an environment that promotes mental well-being and reduces the likelihood of anxiety attacks.
The Role of Nutrition and Exercise in Anxiety Management
Nutrition and exercise play a crucial role in managing anxiety. Research has shown that certain dietary choices and physical activities have a positive impact on mental well-being and can help reduce the frequency and intensity of anxiety attacks.
When it comes to nutrition, it is important to focus on a well-balanced diet that includes foods rich in essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and B vitamins. These nutrients have been found to promote brain health and regulate mood. Incorporating foods like fatty fish, nuts and seeds, leafy greens, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals can help support your mental health. Additionally, reducing the intake of stimulants like caffeine and alcohol may also help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Exercise, on the other hand, is known to be a powerful stress reducer and mood enhancer. Engaging in regular physical activity improves blood flow to the brain, reduces muscle tension, and increases the production of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Whether it’s a brisk walk, a yoga session, or a high-intensity workout, finding an exercise routine that suits your preferences and schedule can greatly contribute to anxiety management. It is recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week for optimal mental health benefits.
While nutrition and exercise alone may not eliminate anxiety attacks, they can be effective tools in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to personalize your nutrition and exercise plan to suit your individual needs and existing health conditions. In the next section, we will explore various techniques and strategies for coping with anxiety attacks in different settings, including the workplace.
Exploring Relaxation Techniques for Coping with Anxiety Attacks
Relaxation techniques play a crucial role in coping with anxiety attacks, as they can help calm the mind and soothe the body. These techniques aim to activate the body’s natural relaxation response, which counteracts the intense feelings of anxiety and stress. By incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine, you can take proactive steps towards managing and preventing anxiety attacks.
One effective relaxation technique is deep breathing exercises. This technique focuses on taking slow, deep breaths, filling your lungs with air to the count of four, and then exhaling slowly to the count of four. Deep breathing helps regulate your heart rate and decrease muscle tension, providing a sense of relaxation and grounding during moments of anxiety.
Another technique that can help ease anxiety is progressive muscle relaxation. This involves systematically tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in your body, starting from your toes and working your way up to your head. Progressive muscle relaxation helps release tension and promote overall relaxation.
Other relaxation techniques that can be beneficial include mindfulness meditation, guided imagery, and gentle physical activities such as yoga or tai chi. By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can create a sense of calm and find relief from the symptoms of anxiety attacks.
Remember, each person may find certain techniques more effective than others, so it’s essential to explore and find what works best for you. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or therapist experienced in anxiety management to tailor relaxation techniques to your specific needs. With dedication and practice, incorporating relaxation techniques into your life can significantly contribute to coping with anxiety attacks and promoting overall well-being.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy as an Effective Approach for Anxiety Prevention
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as a highly effective approach for the prevention and management of anxiety. This evidence-based therapy focuses on identifying and addressing the negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. By understanding the intricate connection between thoughts, feelings, and actions, CBT equips individuals with practical tools to effectively cope with anxiety and prevent future episodes.
One of the key strategies employed in CBT for anxiety prevention is cognitive restructuring. This technique aims to challenge and replace irrational or negative thoughts with more rational and positive ones. By reconstructing these thought patterns, individuals can learn to perceive anxiety-provoking situations in a more realistic and adaptive manner, reducing the intensity and frequency of anxiety attacks. Additionally, CBT helps individuals develop effective coping skills and strategies to manage stress and anxiety, such as relaxation techniques and problem-solving strategies.
Research studies have consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of CBT in anxiety prevention. For instance, a meta-analysis conducted by Hofmann et al. (2012) reviewed 92 studies and found that CBT was more effective than other psychotherapies in reducing anxiety symptoms. Moreover, the benefits of CBT were shown to persist over time, highlighting its potential as a long-term solution for anxiety prevention. With its evidence-based approach and focus on empowering individuals, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy stands as a valuable tool in the fight against anxiety.
Seeking Professional Help: When and How to Reach Out
Seeking professional help for anxiety attacks is an important step in managing and overcoming this challenging condition. While self-help strategies and support from loved ones can be beneficial, the expertise of a qualified mental health professional can provide the necessary guidance and interventions for long-lasting relief. It is crucial to know when and how to reach out for professional help to ensure that you receive the most appropriate and effective treatment.
One key indicator that it may be time to seek professional help is when anxiety attacks significantly interfere with your daily life and functioning. If your symptoms persist or worsen over time, despite efforts to manage them on your own, it may be a sign that professional intervention is necessary. Additionally, if you experience co-occurring conditions such as depression, substance abuse, or chronic physical health problems, seeking professional help can address these complex issues holistically.
Enhancing Self-Care Practices to Reduce Anxiety Attacks
Self-care practices play a crucial role in reducing anxiety attacks and promoting overall mental well-being. By prioritizing self-care, individuals can effectively manage their anxiety symptoms and build resilience to stressful situations. Here are some key strategies to enhance self-care practices and alleviate anxiety:
1. Prioritize relaxation techniques: Incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help to calm your mind and alleviate anxiety. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are effective techniques that promote relaxation and stress reduction. Find a quiet and comfortable space where you can practice these techniques for a few minutes each day.
2. Establish a healthy sleep routine: A good night’s sleep is essential for managing anxiety. Create a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and establish a consistent sleep schedule. Avoid stimulants like caffeine before bed, limit exposure to electronic screens, and create a calm sleep environment to ensure quality and restful sleep.
Remember, self-care practices are unique to each individual, so it’s important to explore different strategies and find what works best for you. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can reduce anxiety and enhance your overall well-being.
Developing a Personalized Coping Plan for Anxiety Prevention
Developing a personalized coping plan for anxiety prevention is an essential step in managing and minimizing the impact of anxiety attacks on your daily life. By creating a comprehensive plan tailored to your unique needs, triggers, and coping mechanisms, you can empower yourself to take control of your anxiety and work towards a healthier state of mind.
The first step in developing your personalized coping plan is to identify your specific anxiety triggers. These triggers can vary greatly from person to person and may include situations, people, or even certain thoughts or fears. Keeping a journal and noting down your emotions and circumstances surrounding each anxiety attack can help you pinpoint recurring patterns and uncover the triggers that contribute to your anxiety. With this awareness, you can then create strategies to either avoid or manage these triggers in a more constructive manner.
Creating a Supportive Environment: Educating Loved Ones about Anxiety Attacks
Creating a supportive environment for individuals experiencing anxiety attacks involves educating loved ones about the nature and impact of these episodes. By increasing awareness and understanding, family members, friends, and partners can become valuable sources of support and comfort during challenging times. It is essential to approach this topic with sensitivity and empathy, as anxiety attacks can be distressing for both the person experiencing them and those around them.
Educating loved ones about anxiety attacks begins with providing them with accurate information about the condition. Anxiety attacks, also known as panic attacks, are intense episodes of overwhelming fear and distress that can manifest with various physical, emotional, and cognitive symptoms. While the specific experience may differ from person to person, symptoms commonly include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, sweating, trembling, feelings of impending doom, and a sense of losing control. Loved ones should understand that these symptoms are not within the person’s control and are not indicative of weakness or lack of resilience. Rather, they are physiological responses triggered by the body’s fight-or-flight response to perceived threats.
To support their loved ones, individuals should learn to recognize the signs of an anxiety attack and respond accordingly. Offer reassurance and understanding, and avoid judgment or criticism. Creating a safe and non-judgmental space for the person to share their experiences can significantly reduce the impact of anxiety attacks. Encourage open communication and active listening, allowing the person to express their emotions and fears without interruption or invalidation. Remember, anxiety attacks can be overwhelming, and sometimes, individuals may not be able to express themselves clearly or coherently. In such situations, providing a calm and understanding presence can be immensely comforting. It’s important to remember that the goal is not to “fix” the anxiety attack but to provide support and reassurance. The person experiencing the attack may find solace in knowing that they are not alone and that their loved ones are there to help them through it.
By fostering a supportive environment and educating loved ones about anxiety attacks, we can promote empathy, understanding, and resilience within relationships. Together, we can create a nurturing and compassionate space that enables individuals to navigate their anxiety more effectively. In the following sections, we will explore additional strategies and resources that can aid in managing anxiety attacks and promoting overall well-being.
What is the first step in educating loved ones about anxiety attacks?
The first step in educating loved ones about anxiety attacks is to understand the nature of anxiety attacks and their symptoms.
How can I recognize the physical symptoms of anxiety attacks?
Physical symptoms of anxiety attacks can include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, and sweating.
What are the emotional signs of anxiety attacks?
Emotional signs of anxiety attacks can include feelings of fear, panic, restlessness, irritability, and a sense of impending doom.
Are there common triggers for anxiety attacks?
Yes, common triggers for anxiety attacks can include stress, certain phobias, traumatic events, and even certain medications or substances.
How does anxiety relate to stress?
Anxiety and stress are closely related, as stress can often trigger or exacerbate anxiety. It is important to manage stress effectively to prevent anxiety attacks.
Can lifestyle factors impact anxiety attacks?
Yes, lifestyle factors such as poor sleep, unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, and excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption can increase the risk of anxiety attacks.
How can anxiety attacks be managed in the workplace?
Strategies for managing anxiety attacks in the workplace include practicing relaxation techniques, setting boundaries, seeking support from colleagues, and implementing stress management techniques.
How can healthy relationships help prevent anxiety attacks?
Nurturing healthy relationships can help prevent anxiety attacks by providing emotional support, reducing feelings of isolation, and promoting a sense of belonging.
What role does nutrition and exercise play in anxiety management?
Nutrition and exercise play a significant role in anxiety management as a healthy diet and regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and promote overall well-being.
Are there specific relaxation techniques that can help cope with anxiety attacks?
Yes, deep breathing exercises, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness techniques are all effective relaxation techniques for coping with anxiety attacks.
Is cognitive-behavioral therapy an effective approach for anxiety prevention?
Yes, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a proven and effective approach for anxiety prevention. It helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety.
When should I seek professional help for anxiety attacks?
It is recommended to seek professional help for anxiety attacks if they significantly interfere with daily life, last for an extended period, or if self-help strategies are not effective in managing the symptoms.
How can self-care practices reduce anxiety attacks?
Engaging in self-care practices such as practicing good sleep hygiene, engaging in hobbies, setting aside time for relaxation, and seeking emotional support can help reduce anxiety attacks.
How can I develop a personalized coping plan for anxiety prevention?
Developing a personalized coping plan for anxiety prevention involves identifying triggers, implementing stress management techniques, seeking professional help if needed, and regularly evaluating and adjusting the plan.
How can I educate my loved ones about anxiety attacks?
To educate loved ones about anxiety attacks, provide them with information about the nature of anxiety attacks, their symptoms, triggers, and available coping strategies. Encourage open communication and empathy.